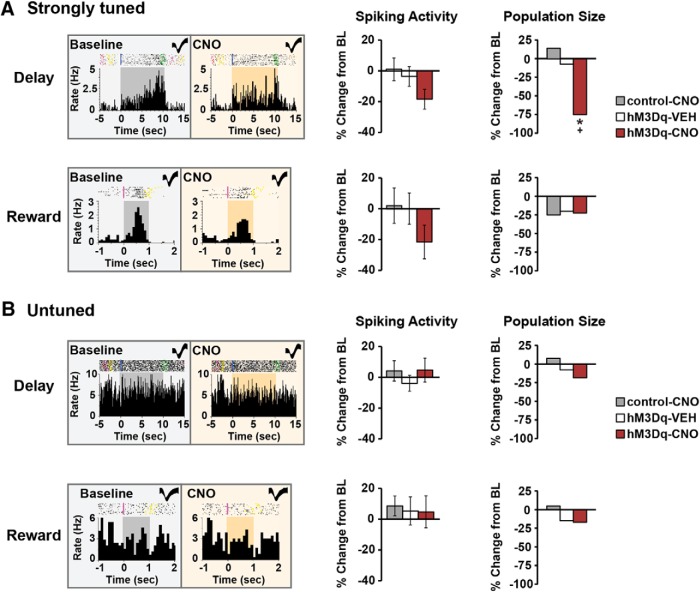
Figure 6.
Effects of PFC CRF neuronal activation on task-related activity of dmSTR MSNs. A, Left, Exemplar rasters/PETHs demonstrating task-related activity of strongly tuned delay (top) and reward (bottom) MSNs under baseline and CNO conditions. Middle, CNO elicited a trend for suppression of task-related activity of strongly tuned delay (n = 12) and reward MSNs (n = 9) in hM3Dq animals that was not observed with vehicle (delay, n = 28; reward, n = 15) or CNO-treated viral controls (delay, n = 28; reward, n = 12). Right, PFC CRF neuronal activation diminished the population size of strongly tuned delay (top), but not reward (bottom), MSNs. B, Left, Exemplar rasters/PETHs of MSNs untuned to delay (top) and reward (bottom) MSNs. CNO elicited no significant effects on task-related activity (middle) or the population size (right) of untuned MSNs in hM3Dq animals (delay, n = 27; reward, n = 35), vehicle-treated hM3Dq animals (delay, n = 26; reward, n = 65), or CNO-treated viral controls (delay, n = 39; reward, n = 61). *p < 0.05 versus control-CNO. +p < 0.05 versus hM3Dq-SAL.