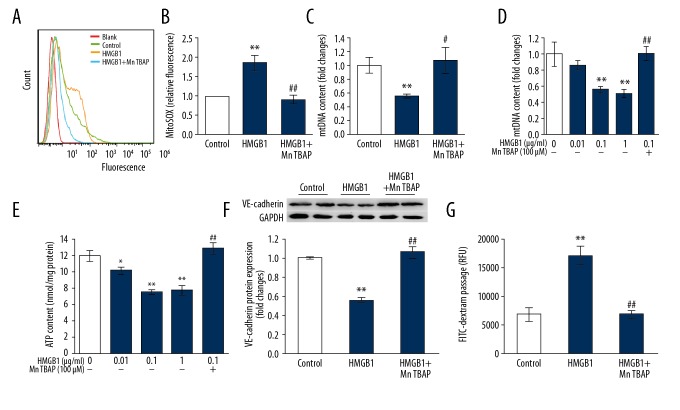
Figure 3.
Mitochondrial oxidative injury participates in HMGB1-induced inhibition of cell adherence junction molecule and endothelial hyperpermeability. (A, B) MitoSOX staining was used to detected mitochondrial superoxide expression followed by analysis using flow cytometry. Both the flow cytometric representative histograms (A) and the results (B) are shown (n=3). (C–G) MLVECs were exposed to HMGB1 (0.1μg/ml) in presence or absence of MnTBAP (100 μM) for 24 h, after which cells were isolated for mtDNA estimation (C), diagnosis of loss of membrane potential of mitochondria (D), and ATP generation (E) (n=4). VE-cadherin protein expression (F) were calculated by Western blot, and permeability of endothelium (G) were estimated by analysis of FITC-dextran flux (n=4). Results are represented as mean ±SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 vs. Control; # p<0.05, ## p<0.01 vs. HMGB1 (0.1 μg/ml).