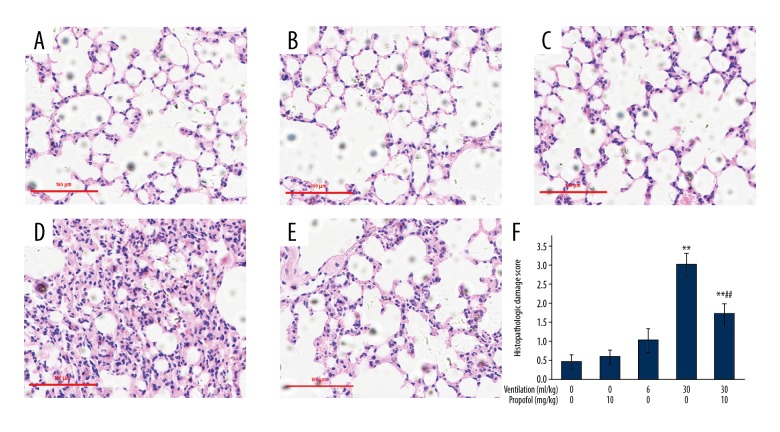
Figure 6.
Propofol use improves pulmonary histopathological alterations caused by ventilation at increased tidal volume. Animals were put on LVT (6 ml/kg) or HVT (30 ml/kg) ventilation for 4 h. Propofol (10 mg/kg) was injected prior to the onset of ventilation, followed by infusion at 5 mg/(kg·h). The left lower lung was surgically isolated for histopathological analysis by HE staining. (A) Control; (B) Propofol treatment; (C) 6 ml/kg Ventilation; (D) 30ml/kg Ventilation; (E) 30ml/kg Ventilation along with propofol treatment. Original magnification, was kept at ×200. Scale bars correspond to 100 μm. (F) The extent of pulmonary injury was scored. Results are presented as mean ±SEM (n=7). ** p<0.01 vs. Control group; ## p<0.01 vs. 30 ml/kg ventilation group.