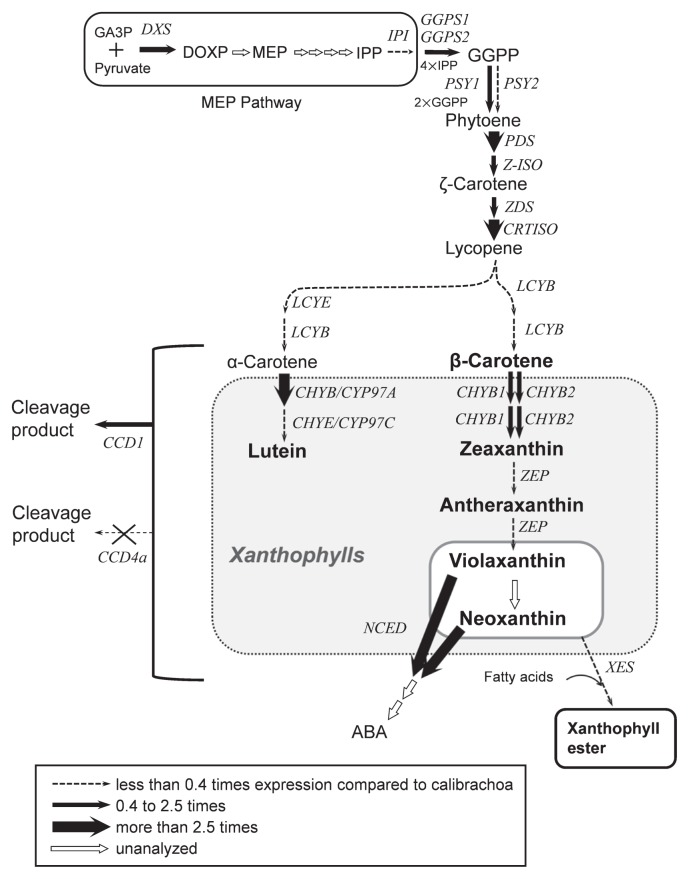
Fig. 5.
Putative carotenoid biosynthetic pathway in corollas of petunia. GA3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase; DOXP, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate; MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodisphosphate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; IPI, IPP isomerase; GGPS, GGPP synthase; GGPP, geranylgeranyl diphosphate; PSY, phytoene synthase; PDS, phytoene desaturase; Z-ISO, 15-cis-ζ-carotene isomerase; ZDS, ζ-carotene desaturase; CRTISO, carotenoid isomerase; LCYB, lycopene β-ring cyclase; LCYE, lycopene ɛ-ring cyclase; CHYB, β-ring hydroxylase; CHYE, ɛ-ring hydroxylase; CHYB/CYP97A, cytochrome P450-type β-ring hydroxylase; CHYE/CYP97C, cytochrome P450-type ɛ-ring hydroxylase; ZEP, zeaxanthin epoxidase; NCED, 9-cis-epoxy carotenoid dioxygenase; ABA, abscisic acid; CCD1, carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 1; CCD4a, carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 4a; XES, xanthophyll esterase. Major carotenoids accumulated in corollas of petunia and calibrachoa are indicated in bold letters. Thickness of arrows indicates the level of gene expression in tubes relative to calibrachoa.