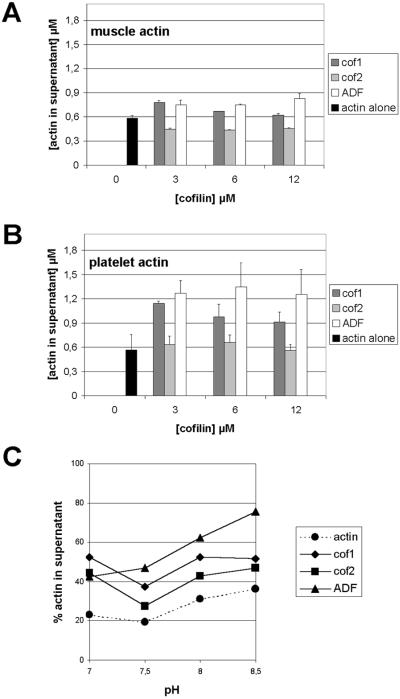
Figure 6.
Ability of ADF/cofilins to shift actin to the monomeric fraction in actin filament sedimentation assay. Muscle (3 μM) (A) or platelet actin (B) were mixed with 0, 3, 6, or 12 μM ADF/cofilins, actin filaments were sedimented by centrifugation, and the amount of actin in the supernatant and pellet fractions was quantified from three independent experiments. This assay was carried out at pH 7.5. Both cofilin-1 and ADF promote significant increases in the amount of monomeric actin and the ability of ADF to disassemble actin filaments is more pronounced with higher protein concentrations. In contrast to cofilin-1 and ADF, cofilin-2 is not able to promote actin filament disassembly. ADF/cofilins shifted more platelet actin (B) to the monomeric pool than muscle actin (A). (C) pH dependency of actin filament disassembly by mouse ADF/cofilins was studied with 3 μM platelet actin and 3 μM ADF/cofilins at pH 7.0–8.5. The ability of cofilin-1 and cofilin-2 to increase the amount of actin monomers is not greatly affected by pH. In contrast, the ability of ADF to disassemble actin filaments is significantly increased at higher pH.