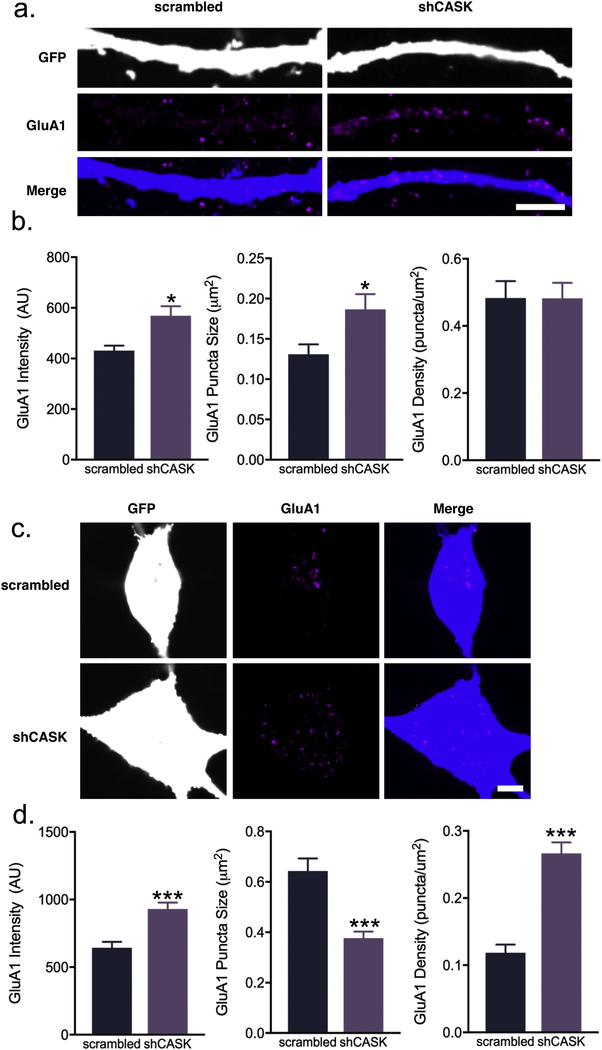
Fig. 4.
CASK knockdown in interneurons leads to alterations of GluA1 content and clustering. (a) Representative confocal images and (b) quantification of GluA1 average intensity, puncta size, and puncta area in scrambled or shCASK-treated (21–26 DIV) rat interneuron dendrites at 26 DIV (scale bar = 5 μ m; intensity: n = 35–36 branches; puncta size and density: n = 33 branches from 3 independent experiments). (c) Representative confocal images and (d) quantification of GluA1 average intensity, puncta size, and puncta area in scrambled or shCASK-treated (21–26 DIV) rat interneuron somas at 26 DIV (scale bar = 5 μ m; n = 20–21 cells from 3 independent experiments). Values are means ± SEM. * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001; Student’s t-test (b, intensity; d), Mann-Whitney test (b, puncta size and density).