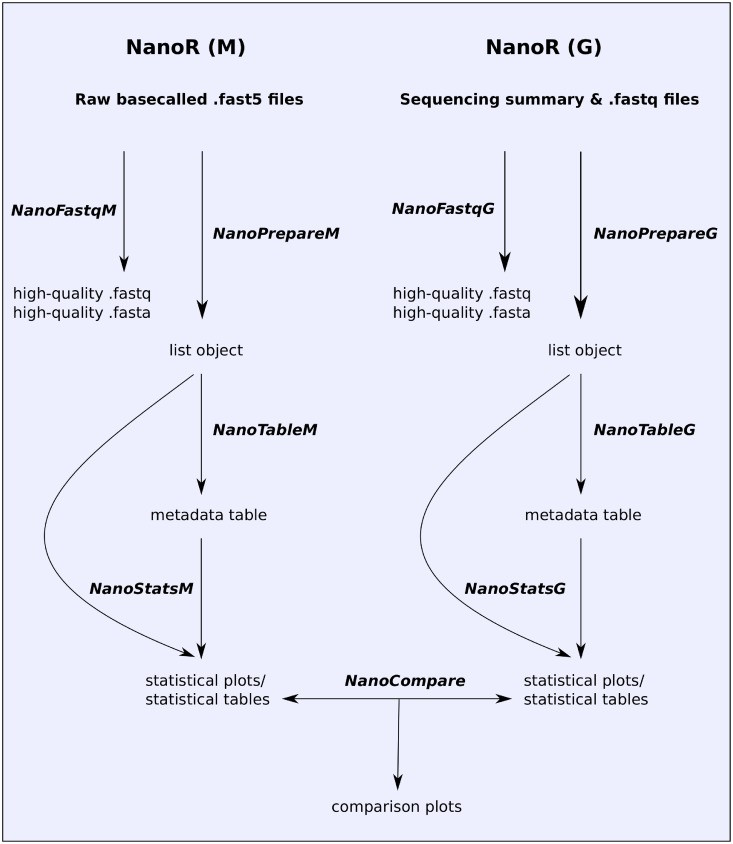
Fig 1. NanoR workflow.
NanoR can work with both basecalled .fast5 files and sequencing summary/.fastq files. Users have to rely on NanoFastqM() to direclty extract .fastq sequences from basecalled .fast5 files and on NanoFastqG() to filter .fastq files. NanoPrepare() functions, as well as NanoTable() and NanoStats() can be used one after another to generate a complete overview for the sequencing run, starting from basecalled .fast5 files (“M” version) or from sequencing summary and .fastq files (“G” version). NanoCompare(), at last, allows one-command comparison of MinION/GridION X5 analyzed sequencing experiments.