Figure 5.
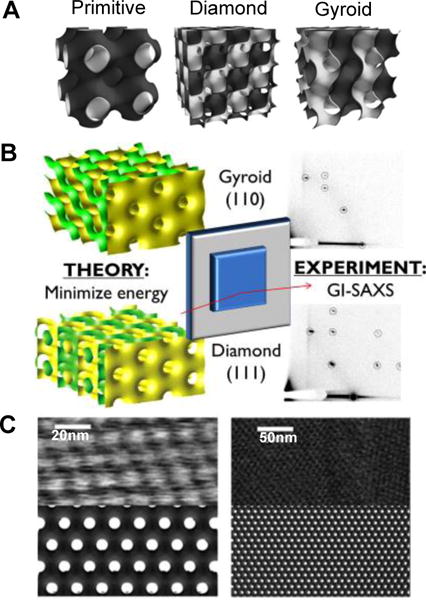
A) Schematic representation of three different bicontinuous cubic phases. The minimal surface represents the mid-plane of a lipid bilayer. Each side of the bilayer has a water domain (represented in dark grey and white) and these domains don’t penetrate. Adapted from [114]. Copyright 2010 The Royal Society of Chemistry B) The crystallographic orientation that cubic phase film adopts with respect to the surface can be predicted from theoretical considerations of surface energy minimization. The predictions are in good agreement with experimental observation. Adapted from [115]. Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society C) AFM images of the diamond cubic phase in water (top) and simulated surface of (111) plane of the cubic diamond phase. The cubic phase films can be directly imaged using AFM. Adapted from [114]. Copyright 2010 The Royal Society of Chemistry.
