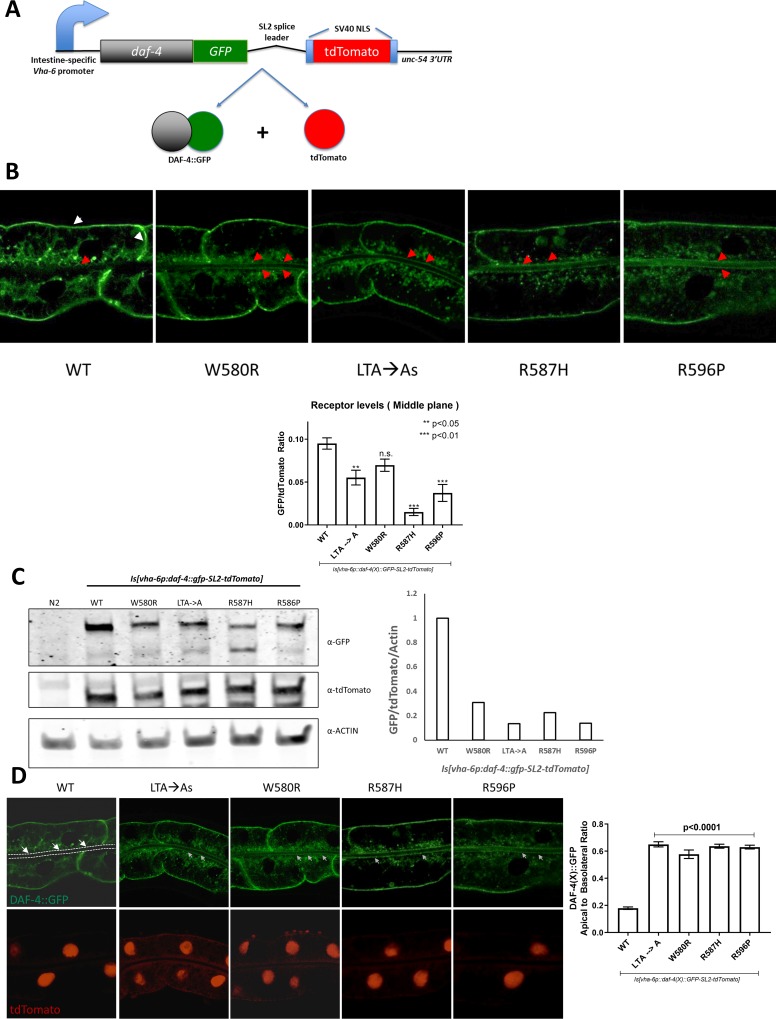
Fig 3.
A. Schematic overview of the transgene construct to study cellular levels and localization patterns of type II TGFβ receptors bearing MFS-like mutations. The SL2 splice leader makes it possible for the one-to-one expression of the DAF-4::GFP and NLS-tdTomato-NLS cassette. This allows precise quantification of the levels of the GFP-tagged DAF-4 receptor. The coding sequences are expressed by the intestine specific Vha-6 promoter. B., C. The LTA → A and MFS-like mutations lead to significantly decreased DAF-4 receptors intracellularly as determined by confocal microscopy (B) and western blot (C). At least six animals were imaged for confocal imaging with three biological replicates per genotype, and quantification of fluorescence intensity was carried out for intracellular abundance. All images have been exposed at the same settings. Graphs indicate mean intensity +/- S.E.M. Statistical comparisons were performed using a One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons against the wild-type strain. Western blot shown is a representative blot from at least three different biological replicates. For Fig 3B, red arrows indicate apical surfaces while white arrows indicate basolateral surfaces. D. Overexposure of the confocal images reveals that the low levels of mutant receptor present intracellularly are mis-trafficked to the apical surface of the intestine (white arrows) as compared to the basolateral surface. Dotted line in WT panel indicates the apical cellular limit. Quantification of the ratio of the apical to basolateral surface is shown in the attached graph. These data indicate that the LTA motif is required for the proper cellular distribution of the DAF-4 receptor and that the MFS-like mutations may disrupt interactions that could affect cellular distribution. Graphs indicate mean intensity +/- S.E.M. Statistical comparisons were performed using a One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons against the wild-type strain.