Figure 1.
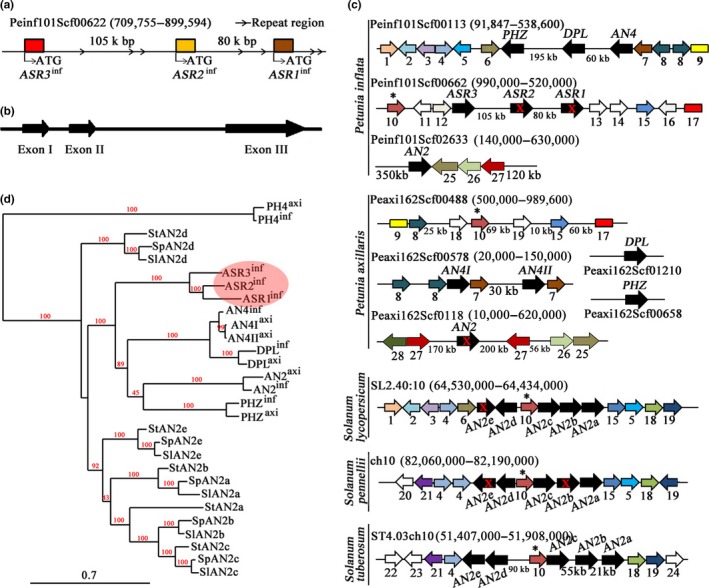
ASR genes cluster in Petunia. (a) The genomic fragment containing the ASR cluster in P. inflata. (b) Architecture of ASR genes in P. inflata. Exons are shown as arrow boxes. (c) Synteny analysis of the genomic regions containing SG6 MYB genes (black arrows) in Petunia and in three Solanum species. Arrows indicate genes and lines gene‐poor regions. Drawings are not to scale. Conserved genes are indicated by the same color. Red crosses indicate mutations in coding sequences that result in inactive proteins. The genes or sequences appearing here were summarized in Supporting Information Table S2. Among these genes, a much conserved gene (asterisk) for a heavy metal associated protein (10) is located in the genomic fragment in which SG6 genes are present in both Petunia and all Solanum species included in this analysis. (d) Phylogenetic analysis of the anthocyanin MYB genes in three Solanum and two Petunia species (genomic DNA sequences including introns). All of the Solanum genomic sequences were obtained from the SOL Genomic Network (https://solgenomics.net/). More information about the sequences used here is given in Supporting Information Table S3
