Figure 3.
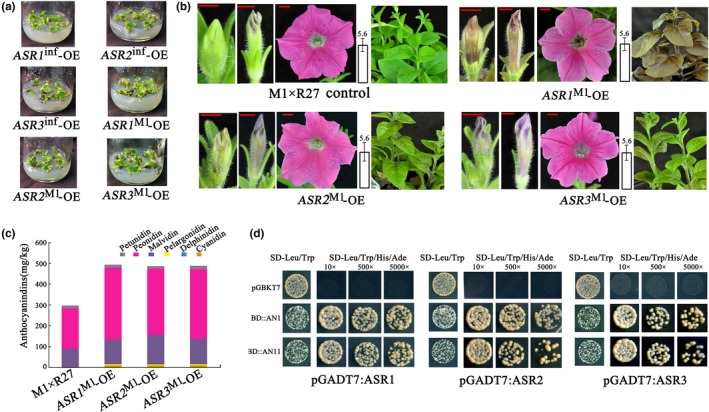
ASR1 M1, ASR2 M1, and ASR3 M1 all induce anthocyanin accumulation in different plant parts, and when ectopically expressed, are functionally similar. (a) Calli transformed with 35S:ASR1 M1 are strongly pigmented, whereas those transformed with 35S:ASR1 inf (inactive allele) show no pigmentation. (b) Pigmentation induced by the expression of ASRs in seedlings of transgenic lines in the hybrid M1×R27 between two Petunia hybrida lines. Petal phenotype at development stage 2, 4, and 7. Red size bars equal 5 mm. On the right of each panel is the pH value of the crude petal extract at development stage 7 (after bud opening). (c) Anthocyanin accumulation in ASRs M1‐OE petals at development stage 2–3, when no obvious color is yet visible in buds of untransformed controls. Anthocyanin levels are indicated as the mean of three biological replicates. Variation in biological replicates is less than 5%; therefore no error bar is shown here. (d) Interaction of ASRsM1 with AN1 and AN11 tested by a yeast two‐hybrid assay. The dilution series (10×, 500×, and 5,000×) were grown for 3 days before being photographed [Correction added on 31 January 2019, after first online publication: in the original version of Fig. 3a the same image was inadvertently used for ASR1M1‐OE and ASR2M1‐OE. This has now been amended.]
