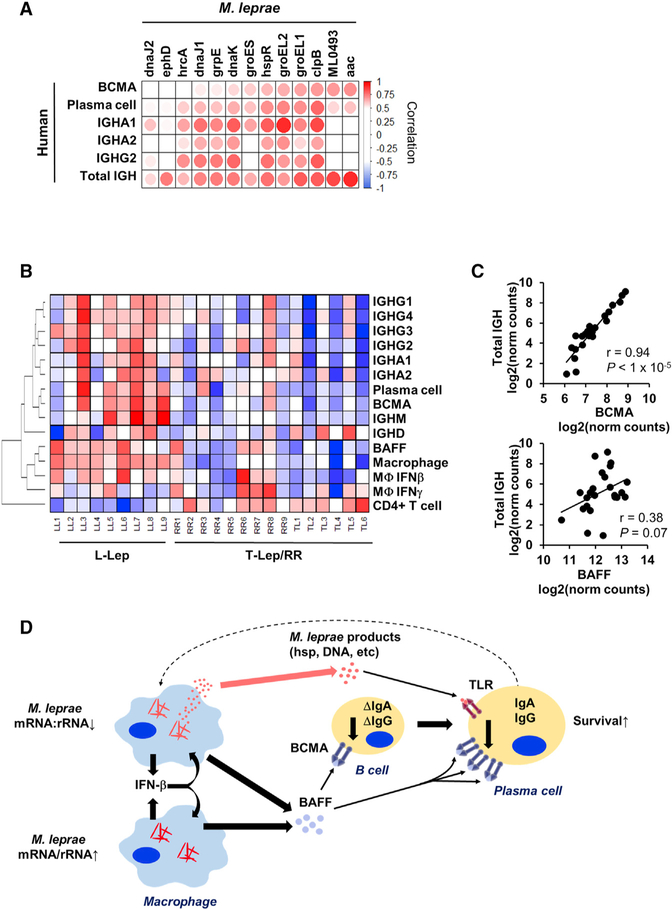
Figure 5. Bacterial Stress Proteins Are Linked to BAFF-BCMA-Induced Antibody Expression.
(A) Correlation heatmap of MLEPblue virulence and heat shock genes (columns) versus MLEP mRNA:rRNA and components of the host antibody response. Positive or negative Pearson correlation indicated by red or blue, respectively (n = 9).
(B) Heatmap of expression of human immune response components across the spectrum of leprosy clinical subtypes (n = 24). Color represents the Z score across each row with red as high and blue as low relative expression.
(C) Correlation plot of the total IGH abundance versus BCMA or BAFF expression across the spectrum leprosy samples (L-lep, T-lep, and RR). p value by Student’s t test (n = 24).
(D) Model for interaction between the pathogen and host humoral response. The model shows that bacterial abundance is correlated with induction of IFN-β leading to BAFF expression. At the same time, decreased M. leprae mRNA:rRNA is linked to the expression of M. leprae heat shock proteins, which can trigger TLR4 activation on plasma cells to upregulate the BAFF receptor BCMA. The BAFF-BCMA interaction results in maturation and survival of class-switched antibody plasma cells.