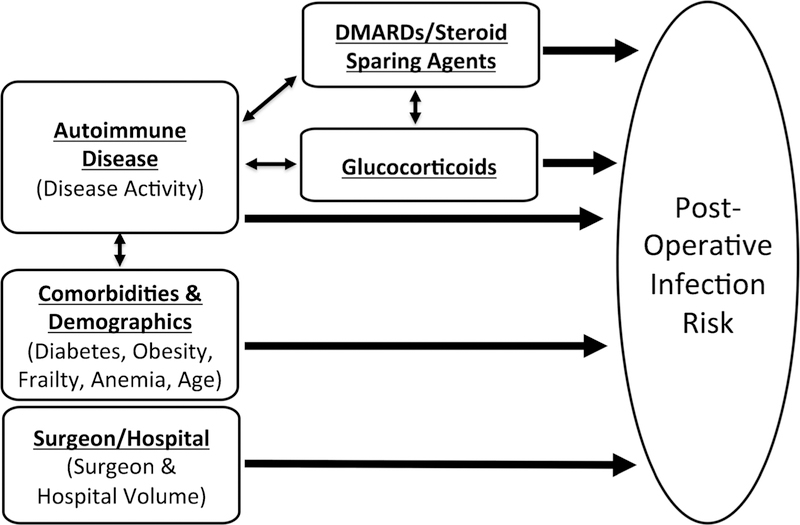
Fig. 1.
Contributors to post-operative infection risk in patients with autoimmune rheumatic disease. Both the disease activity and the immunosuppression used to treat the disease (conventional therapies, biologic/targeted therapies, and especially glucocorticoids) are contributors to post-operative infection risk and are interconnected. Comorbidities (some of which can be affected by the underlying autoimmune disease), demographics, and surgeon and hospital volume are also important contributors to post-operative infection risk and are important to consider when evaluating a patient planning surgery. DMARDs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs