Figure 1.
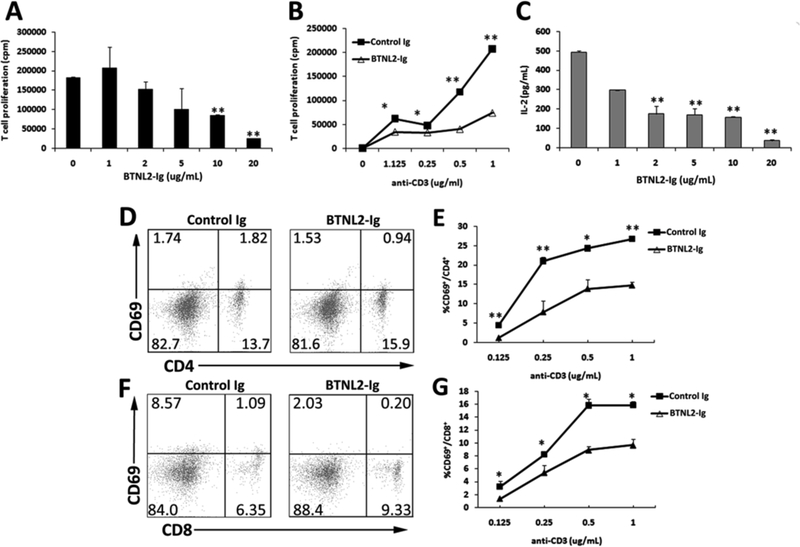
rBTNL2-Ig inhibits T cell function from NOD mice in vitro. Purified CD3+ T cells were stimulated with (A, C) 1 µg/ml plate bound anti-CD3, or (B, D-G) varying concentrations of anti-CD3 in the presence of indicated concentrations of rBTNL2-Ig or control Ig protein for (D-G) 12 h (for early T cell marker CD69 detection), or (A-C) 72 h (for T-cell proliferation and IL-2 production). (A, B) For the T-cell proliferation assay, the cells were pulsed with 1 µCi of [3H]-thymidine 12 hours before harvest. (C) The levels of IL-2 in the supernatant were measured by an ELISA kit. (D-G) T cells were examined for CD69 expression by CD4 and CD8 T cells by flow cytometry. (D, F) Representative flow cytometric profiles and (E, G) are statistical analysis of the percentages of CD69+ cells in CD4 or CD8 T cells. Data represent three independent experiments and are expressed as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 vs control Ig.
