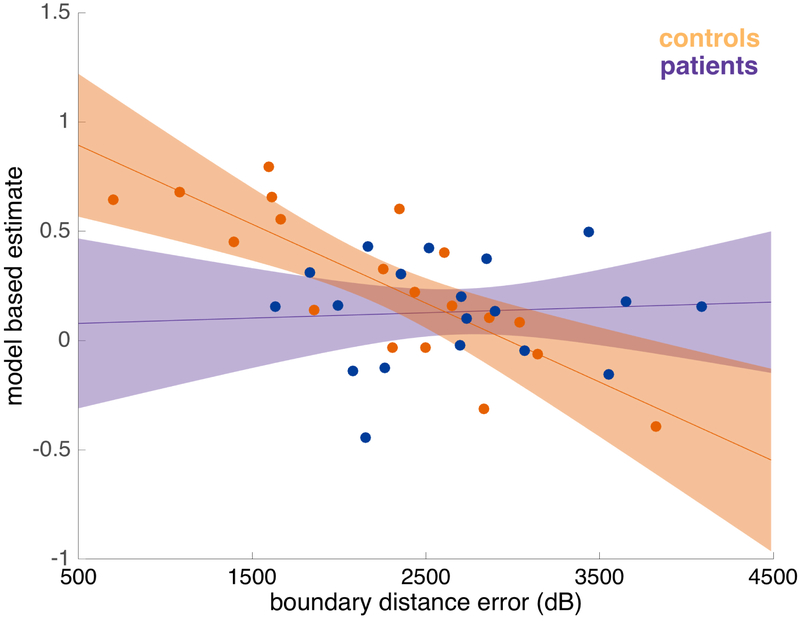
Figure 6: Relationship between model-based planning and boundary distance error (arbitrary unit) in controls and patients.
Estimated with a logistic mixed-effects regression, controlling for IQ. Error bars indicate 80% confidence intervals. Individual place memory performance is reflected by mean boundary distance error (dB) from the spatial task. Dots indicate estimates for individual participants, calculated from the mixed-effects logistic regression. The trend was significant in the control group (z=6.6455, p= 0.001), but not in the left patient group (z=0.156, p=0.875). The slope differed significantly between groups (z=2.137, p=0.032).