Figure 1. Functional antagonism of α3β4* nAChRs reduces THC withdrawal signs.
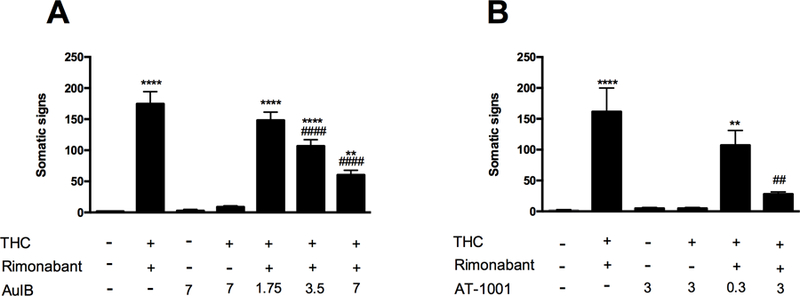
(A) THC-dependent mice pretreated with the selective α3β4* nAChR antagonist, AuIB (1.75, 3.5, 7 pmol, i.c.v.), show a decrease in somatic signs compared with the group of mice injected with THC and rimonabant. The injection of AuIB (7 pmol/mouse, i.c.v.) by itself or in combination with THC does not affect the total somatic signs compared to vehicle-treated group. ****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01 versus vehicle+vehicle+vehicle group; ####P < 0.0001 versus THC+rimonabant+AuIB (1.75 pmol) group. (B) The partial agonist, AT-1001 (0.3, 3 mg/kg, i.p.), dose-dependently decrease the total somatic signs compared to the group of mice injected with THC and rimanabant. The injection of AT-1001 (3 mg/kg, i.p.) by itself or in combination with THC does not affect the total somatic signs compared to vehicle-treated group. **** P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01 versus vehicle+vehicle+vehicle group; ##P < 0.01 versus THC+rimonabant+AT-1001 (0.3 mg/kg) group. Data reflect mean ± SEM, n=8 mice per group.
