Figure 3. THC withdrawal signs require α6, but not α7 or β2, nAChR subunits.
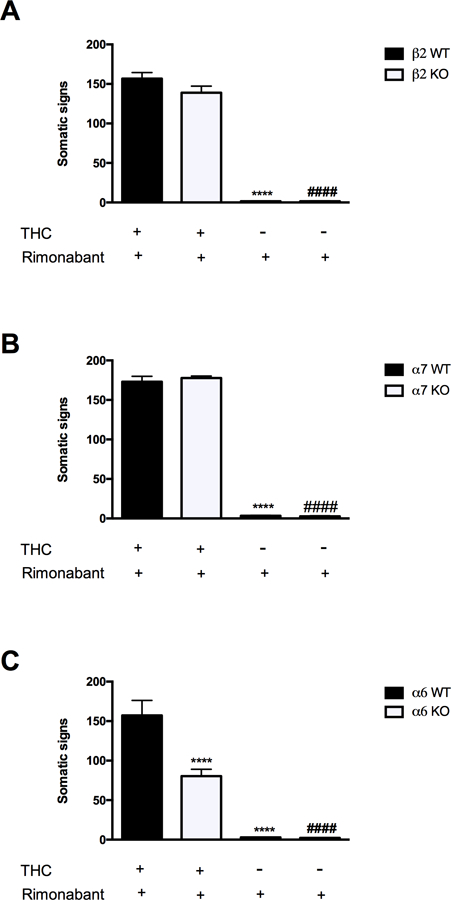
(A) Both THC-dependent β2 nAChR WT and KO mice show an increase in total somatic signs when challenged with rimonabant. ****P < 0.0001 versus β2 WT (THC+rimonabant) group; ####P < 0.0001 versus β2 KO (THC+rimonabant). Data reflect mean ± SEM, n=10 mice per group. (B) α7 nAChR WT and KO mice display the same increase in somatic sign after THC and rimonabant injection. **** p < 0.0001 versus α7 WT (THC+rimonabant) group; ####P < 0.0001 versus α7 KO (THC+rimonabant). Data reflect mean ± SEM, n=11–12 mice per group. (C) Compared to α6 WT mice, α6 nAChR KO mice show a significant reduction in THC withdrawal. The injection of rimonabant alone in β2, α7, and α6 WT and KO mice does not alter the physical THC withdrawal signs compared to the respective vehicle-treated groups. ****P < 0.0001 versus α6 WT (THC+rimonabant) group; ####P < 0.0001 versus α6 KO (THC+rimonabant). Data reflect mean ± SEM, n=11–12 mice per group.
