Figure 6. Nlgn1 Binding to Neurexins is Essential for Structural and Functional VGCC-dependent LTP.
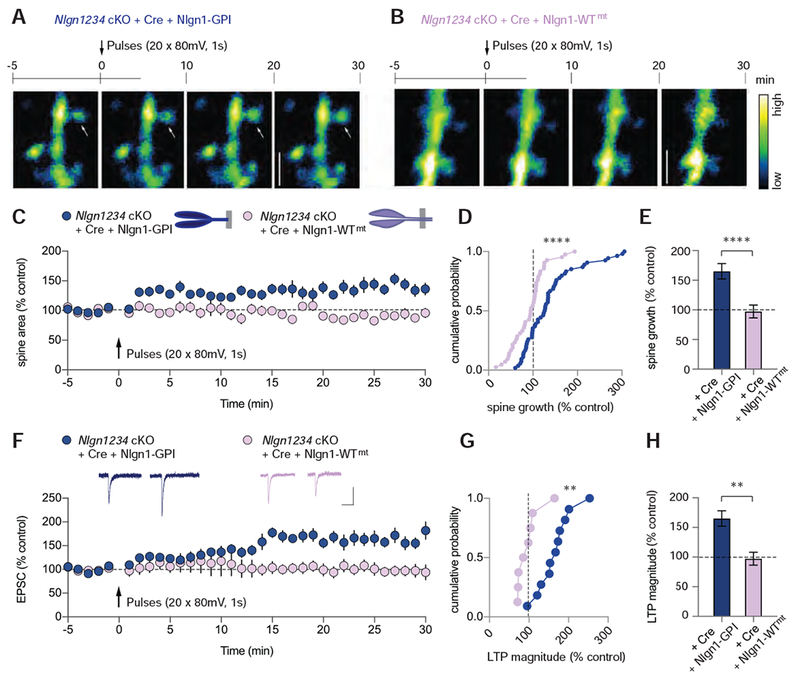
(A) (A, B) The time course of experiments with representative two-photon images of dendritic segments from Nlgn1234 cKO slices infected with AAV-DJ-CMV-DIO-EGFP (cytoplasmic) and (A) lentiviral Cre-EGFP + Nlgn1-GPI or (B) Cre-EGFP + Nlgn1-WTmt. White arrow indicates an example spine that grew relative to baseline. Bar on right displays the color coding reflecting the degree of fluorescence intensity. Scale bar: 2.5 μm
(C) Summary time course of spine growth comparing Nlgn1-GPI rescue with Nlgn1-WTmt rescue.
(D) Cumulative frequency plot of changes in spine area for all imaged spines in the two conditions.
(E) Quantification of spine growth magnitude (mean ± SEM; numbers = spines/cells).
(F) Summary time course of EPSCs following induction of VGCC-dependent LTP. Insets show sample traces pre- and post-pulses (Scale bars: 50 pA, 50 ms).
(G) Cumulative frequency plot of LTP magnitude for individual cells.
(H) Quantification of LTP magnitude (mean ± SEM; numbers = cells/animals). Mann Whitney test,**p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.
