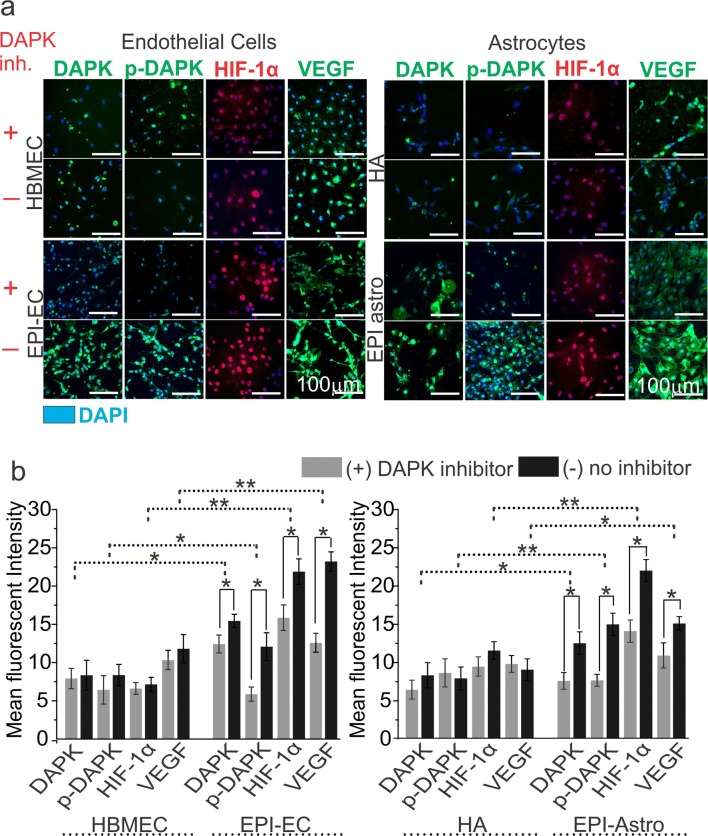
Fig. 4.
Association of DAPK with p-DAPK, HIF-1α, and VEGF expression in brain endothelial cells (ECs) and astrocytes. a Inhibition of DAPK was confirmed by decreased expression of DAPK in the ECs and astrocytes by immunocytochemistry staining. DAPK inhibition caused subsequent inhibition of p-DAPK, HIF-1α, and VEGF expression in the brain ECs and astrocytes. The inhibition was more pronounced in EPI-ECs and EPI-Astro compared to control ECs (HBMECs) and control-Astro cells (HA), respectively. The total number of cells were identified by DAPI-nuclear labelling in blue. b Quantification confirms nonsignificant alterations with and without DAPK inhibition on p-DAPK, HIF-1α, and VEGF expression in HBMEC and HA. However, a significant decrease in p-DAPK, HIF-1α, and VEGF levels was observed post DAPK inhibition on EPI-ECs (*p < 0.05). Similarly, EPI-Astro cells showed a significant reduction in p-DAPK and VEGF expression (*p < 0.05) with DAPK inhibition. Consistent elevation in DAPK, p-DAPK, and VEGF expression was found in EPI-ECs and EPI-astro cells compared HBMEC and HAs, respectively without DAPK inhibition. Data is expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ANOVA, analysis of variance