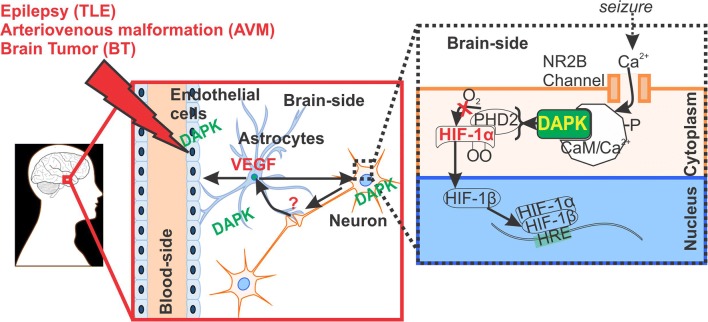
Fig. 7.
Pathophysiological implication of DAPK regulation at the neurovascular interface. DAPK overexpression identified in the neurons, astrocytes and in brain ECs (EC) microcapillaries may possibly be linked to HIF-1α and VEGF function in brain pathologies triggered by seizures and/or associated with BBB dysfunction. It is known that HIF-1α is activated in ECs and neurons in response to hypoxia [5, 19–21], as shown schematically. Astrocytes receives signals from neurons under hypoxic stress and release VEGF to induce angiogenesis at the neurovascular interface in such brain disorders. DAPK could possibly have a dual role and also indicative of cell survival in disease state (such as epilepsy) cannot be ruled out, which needs further investigation