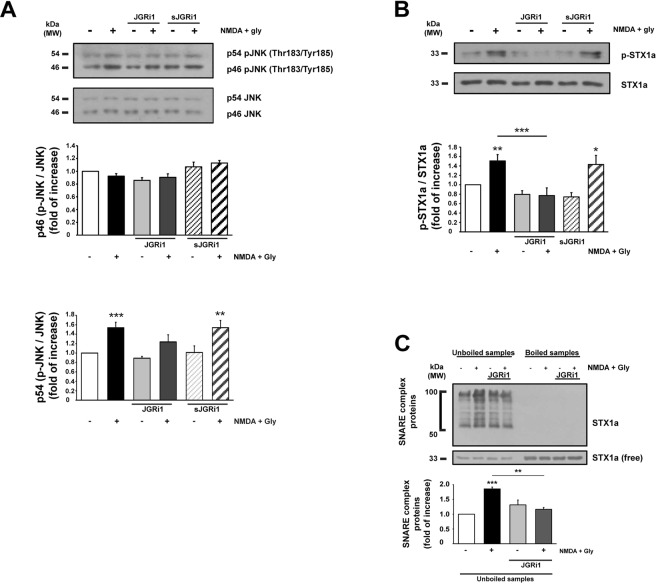
Figure 4.
(A) p46-JNK and p54-JNK level measurement. p46-JNK was not affected by treatments while p54-JNK was increased after 10 min NMDA (100 μM) + glycine (1 μM) alone or pre-treated with JGRi1 (1 μM) or sJGRi1. JGRi1 (1 μM) or sJGRi1 (1 μM) alone did not affect JNK phosphorylation state. Means ± s.e.m. n = 7, ***p < 0.001 NMDA stimulus vs. control, **p < 0.01 NMDA + sJGRi1 vs. control; Newman-Keuls’s test. Cropped WBs are here shown. (B) NMDA stimulus increased STX1a phosphorylation that was instead prevented by pretreatment with JGRi1 (1 μM), but not by sJGRi1 (1 μM). Means ± s.e.m. n = 7, *p < 0.01 NMDA stimulus vs. control, ***p < 0.001 JGRi1 alone vs NMDA, ***p < 0.001 NMDA + JGRi1 vs NMDA, *p < 0.05 NMDA + sJGRi1 alone vs. control; Newman-Keuls’s test. Cropped WBs are here shown. (C) Where indicated JGRi1 (1 μM) was applied to cortical synaptosomes 30 min before 10 min NMDA (100 μM) + glycine (1 μM) stimulus. SNARE complex formation was assessed by probing STX1a in unboiled samples comparing STX1a lanes smearing (50 to 100 kDa) with free STX1a in a cropped WB. NMDA increased SNARE complex formation while JGRi1 prevented it. Means ± s.e.m. n = 4, ***p < 0.001 NMDA stimulus vs. control, **p < 0.01 JGRi1 alone vs NMDA; Newman-Keuls’s test.