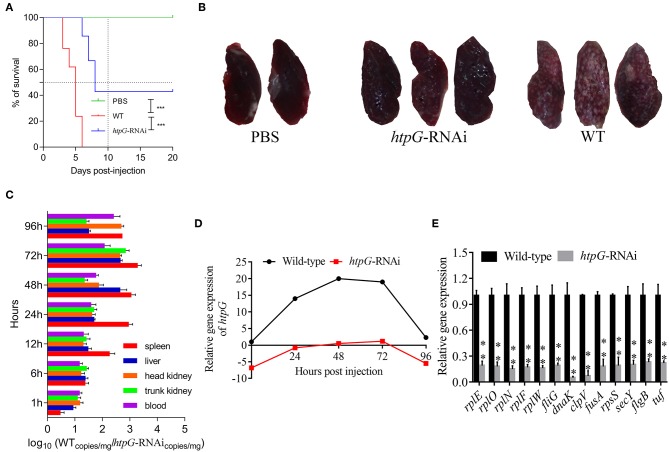
Figure 2.
The virulence of wild-type and htpG-RNAi strain of P. plecoglossicida. (A) Survival rate of E. coioides infected by P. plecoglossicida (n = 3). (B) Symptoms of spleen of E. coioides infected by P. plecoglossicida. (C) Spatial and temporal distribution of htpG-RNAi strain compared to wild-type strain. (D) Expression level of htpG of P. plecoglossicida in the spleen of E. coioides. (E) qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of randomly selected novel genes among wild type P. plecoglossicida in vitro, wild type P. plecoglossicida in vivo, and htpG-RNAi strain in vivo. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001.