Figure 1.
Firing of Cortical PV Interneurons and Thalamic VPM Nucleus during Up and Down States
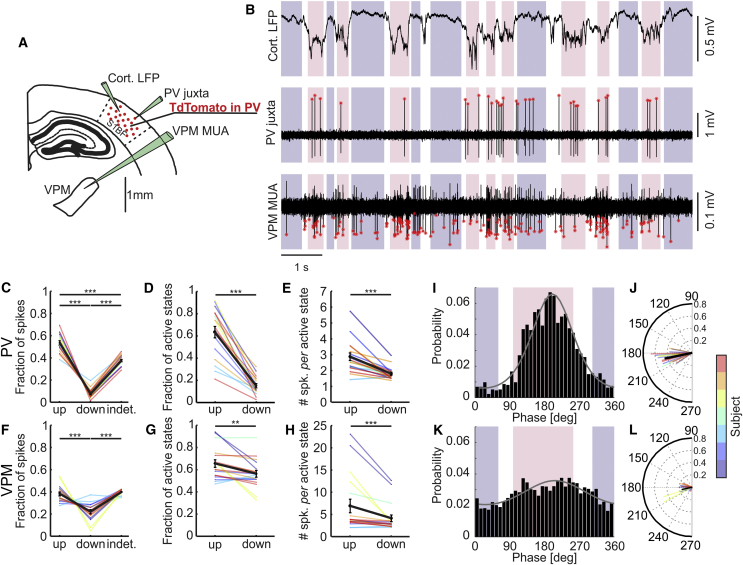
(A) Schematic of the experimental configuration. Two-photon guided juxtasomal recordings of PV interneurons in S1bf were conducted while recording the LFP in S1bf and the MUA in the VPM.
(B) Representative traces of cortical LFP (top), single-unit activity from a PV interneuron (middle), and thalamic MUA (bottom) during up and down states. Pink and purple in the background indicate up and down states identified from the LFP, respectively. White indicates indeterminate states (see STAR Methods). Red asterisks mark detected spikes.
(C) Fraction of action potentials fired by PV cells in up, down, and indeterminate periods (up-down p = 2.8E−11; up-indeterminate p = 0.00015; down-indeterminate p < 2E−16; paired Student’s t test; Bonferroni corrected; n = 18 cells from 7 animals) relative to the total number of PV spikes. In this as well in other figures, colored dots and lines identify individual cells. Black dots and lines indicate the average value across cells. Error bars indicate SEM. Not significant (n.s.), p > 0.05; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(D) Fraction of active up states and active down states relative to the total number of up and down states, respectively (p = 4.65E−9; paired Student’s t test; n = 18 cells from 7 animals).
(E) Average number of spikes fired by PV cells per single up or down state (p = 2.82E−5; paired Student’s t test; n = 18 cells from 7 animals).
(F–H) Same as in (C)–(E) but for thalamic MUA. In (F), up-down p = 0.00086, up-indeterminate p = 0.95020, down-indeterminate p = 4.7E−7; paired Student’s t test; Bonferroni corrected; n = 18 recordings from 7 animals. In (G), p = 0.008; paired Student’s t test; n = 18 recordings from 7 animals. In (H), p = 7.98E−4; Wilcoxon signed-rank test; n = 18 recordings from 7 animals.
(I) Phase of firing distribution for one representative PV interneuron. Pink and purple indicate the range of phases corresponding to up and down states, respectively. The gray line shows the von Mises fit (see STAR Methods; μ = 188° and κ = 1.38). The preferred phase of firing (see STAR Methods) was 192 ± 13 degrees (circular mean ± angular deviation; n = 18 cells in 7 animals) and the locking strength 0.461 ± 0.006 (n = 18 cells in 7 animals).
(J) Circular plot of the mean phase of firing of PV interneurons. The thick black line indicates the overall mean phase of firing and average locking strength (n = 18 cells from 7 animals).
(K and L) Phase of firing distribution for one representative VPM MUA (K) and circular plot of the mean phase of firing for all recorded VPM MUA signals (L). VPM MUA was simultaneously recorded together with the cortical PV interneuron. The preferred phase of firing of the 16 out of 18 phase-locked VPM MUA recordings was 191 ± 23 degrees (n = 16 cells in 6 animals), not different from that of simultaneously recorded PV interneurons (Watson-Williams test; p = 0.92; n = 16 in 6 animals).
See also Figure S1.