Figure 4.
Increased Latency of Optogenetic-Evoked Down-to-Up Transitions upon Thalamic Inactivation
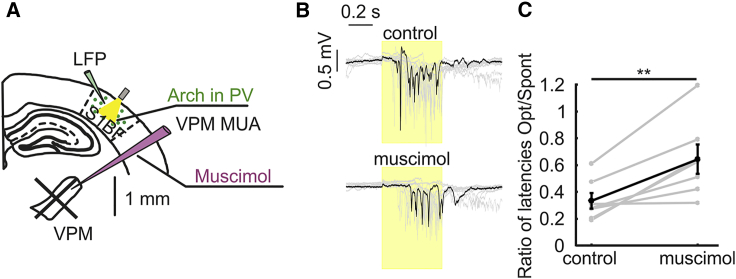
(A) Schematic of the experimental configuration. The inhibitory opsin Arch was expressed in PV cells located in S1bf (green circles). Cortical LFP was recorded via a glass electrode. Thalamic inhibition was achieved through local injection of muscimol.
(B) Representative cortical LFP traces under control conditions (top) and after muscimol injection in the thalamus (bottom), showing the effect of optogenetic inhibition of cortical PV interneurons (yellow bar).
(C) Ratio between light-evoked down-to-up transition latencies and spontaneous down-to-up transition latencies under control conditions and after muscimol application (n = 7 animals; p = 7.8E−3; Wilcoxon signed rank test).
See also Figure S4.