Figure 4.
MRJP-3 RNP Granules Protect RNA From Degradation and Enhance RNA Bioavailability
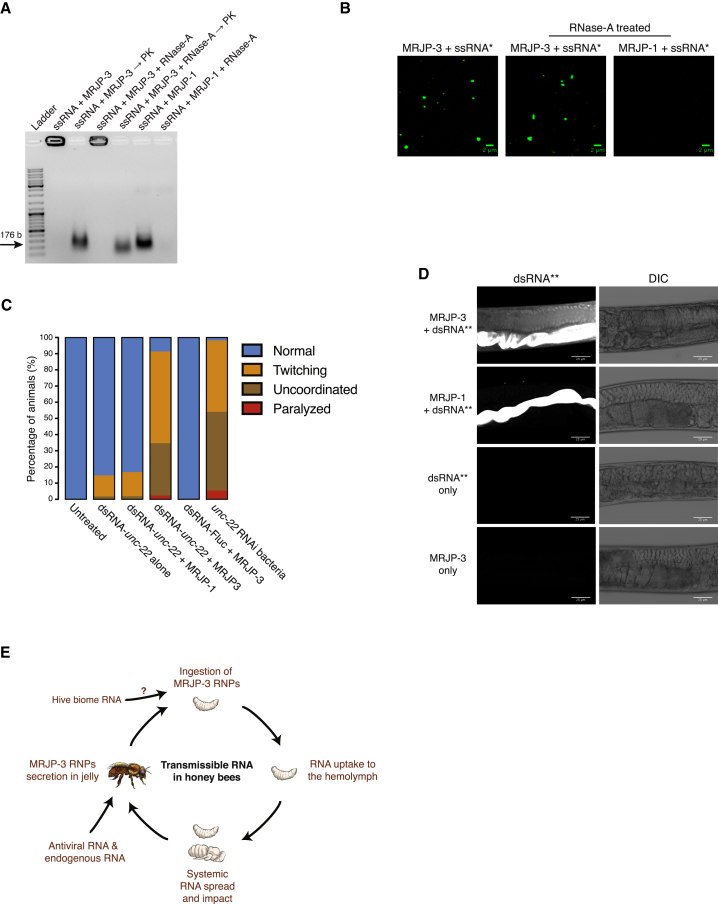
(A) MRJP-3-bound RNA is protected from RNase-A digestion. Treatments included ssRNA mixed with MRJP-3, ssRNA mixed with MRJP-3 followed by incubation with PK, ssRNA mixed with MRJP-3 and RNase-A, ssRNA mixed with MRJP-3 and RNase-A followed by incubation with PK, ssRNA mixed with MRJP-1, and ssRNA mixed with MRJP-1 and RNase-A. ssRNA (0.3 μM) and MRJP-3 or MRJP-1 (42.8 μM) were used in all ssRNA- and protein-containing treatments. RNase challenge was performed by introducing 5 μg RNase-A followed by 1 h incubation at room temperature.
(B) RNase-A presence does not affect MRJP-3 RNPs. Images of RNPs formed with ssRNA∗ with or without RNase-A. ssRNA∗ (0.3 μM) and MRJP-3 or MRJP-1 (42.8 μM) were used in all ssRNA∗- and protein-containing treatments. RNase challenge was performed by introducing 5 μg RNase-A followed by 1–3 h incubation at room temperature. Scale bar represents 2 μm.
(C) dsRNA-MRJP-3 RNPs enhance unc-22 RNAi phenotype in C. elegans. Each treatment contained three biological repeats (n = 150 animals per treatment).
(D) MRJP-3 RNPs enhances ingested dsRNA uptake in C. elegans. Animals were soaked in the presence of MRJP-3 RNPs formed with Alexa Fluor-647-labeled dsRNA-Fluc (dsRNA∗∗). Control groups included soaking animals with dsRNA∗∗ mixed with MRJP-1, dsRNA∗∗ mixed in RJ buffer, and MRJP-3 alone. dsRNA∗∗ (2.15 nM) and MRJP-3 or MRJP-1 (42.8 μM) were used in all dsRNA- and protein-containing treatments.
(E) A working model describing the role of MRJP-3 in the transmissible RNA pathway in honeybees. Nurse bees secrete jelly-containing RNPs that comprise endogenous and exogenous (e.g., viral, fungi, bacteria, plant) RNAs. Bee larvae ingest environmental MRJP-3 RNPs through jelly consumption. The ingested RNA is taken up to the hemolymph, is systemically spread, and affects gene expression including an antiviral response.
See also Figure S4.