Figure 2.
Krüppel-like Factors Are Major Inducers of EGA and Naive-Specific TE Enhancers
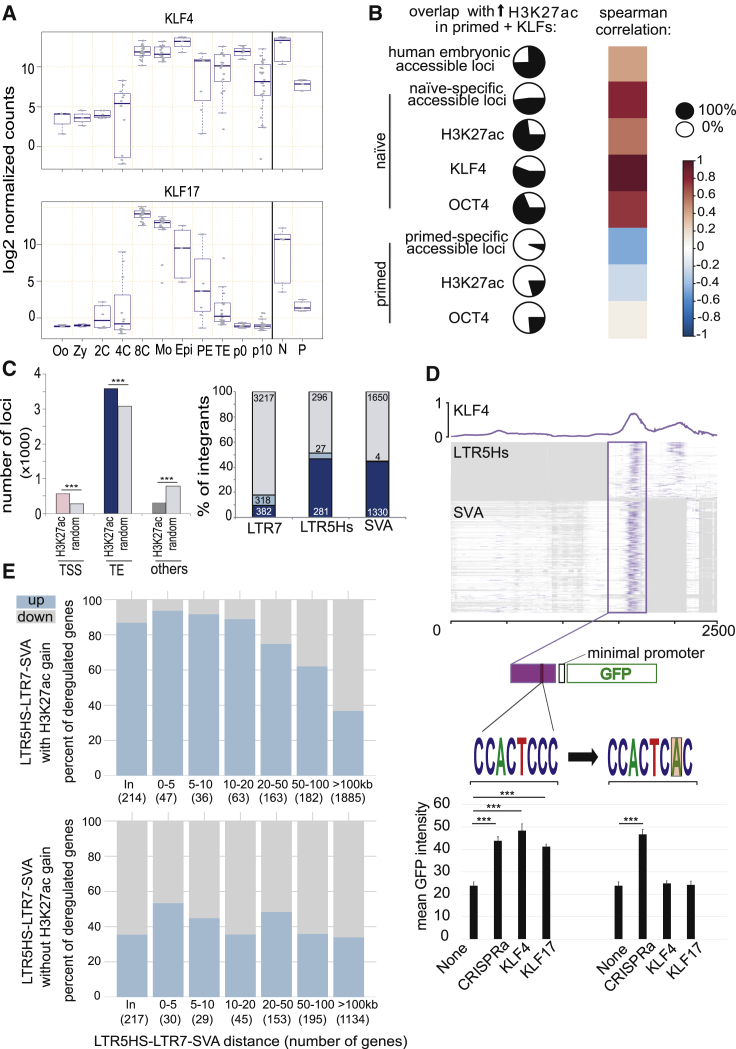
(A) KLF4 and KLF17 expression during early human embryonic development and stem cells, determined by re-analyzing single-cell RNA-seq data from Yan et al. (2013). Single-cell data points are grouped according to developmental stage: oocytes (Oo); zygotes (Zy); 2-cell (2C); 4-cell (4C); 8-cell (8C); morula (Mo); with late blastocyst split into epiblast (Epi), primitive endoderm (PE), and trophectoderm (TE); p0 and p10 representing passage numbers of ESCs derived from blastocyst and naive (N) and primed (P) hESCs (Theunissen et al., 2016).
(B) Pairwise comparison of KLF4/17-induced acetylation loci. H3K27ac ChIP was performed 5 days after transducing primed hESCs with GFP-, KLF4-, or KLF17-expressing lentiviral vectors, thus identifying H3K27ac loci with increased signal (n = 4,446; adjusted p value < 0.05); pie charts represent its proportion (black part; in % of the 4,446 loci) overlapping with chromatin accessibility in hESCs (determined by ATAC-seq, with naive versus primed specific loci defined by ≥2-fold difference with adjusted p < 0.05), human embryo DNase-seq, H3K27ac (K27ac), and OCT4- or KLF4-enrichment (p < 10e−5) in indicated cells. Color scale corresponds to Spearman correlation of pairwise loci comparisons.
(C) Genomic distribution of increased H3K27ac loci upon KLF4/17 overexpression in primed ESCs. (Left) Distribution between TSS (±500 bp) of coding genes and the non-TSS overlapping loci is shown: TEs (50% overlap from either TE or H3K27ac peak) or other regions; p values were computed with a permutation test (1,000 permutations); (right) distribution within indicated TE subfamilies with (blue) and without (gray) gain of H3K27ac enrichment is shown, further depicting loci with (light blue) or without (dark blue) increase expression in GFP versus both KLF4 and KLF17 (adjusted p value < 0.05). Numbers of integrants are indicated for each category.
(D) KLF4 binding on LTR5Hs and HERVK (SINE-R) region of SVA. KLF4 ChIP-seq signal in naive hESCs was superimposed on multiple sequence alignment of corresponding TEs. The rectangle highlights the common enhancer piece bound by KLF4, the one which was cloned from a SVA into a GFP vector activatable by CRISPRa, but not by KLF4 or KLF17 when KLF-motif is mutated. Error bars were established using SEM and p value using t test (∗∗∗ ≤ 0.001). See STAR Methods for details.
(E) KLF4-KLF17 overexpression in primed ESCs activates TE-close genes. Proportion of up- and downregulated genes upon KLF4-KLF17 overexpression is shown (y axes; p < 0.05), according to their distance to the closest TE (x axes). Upper and lower panels use TEs (SVA, LTR5Hs, and LTR7) with or without H3K27ac gains upon KLF4-KLF17 overexpression, respectively.