Figure 1.
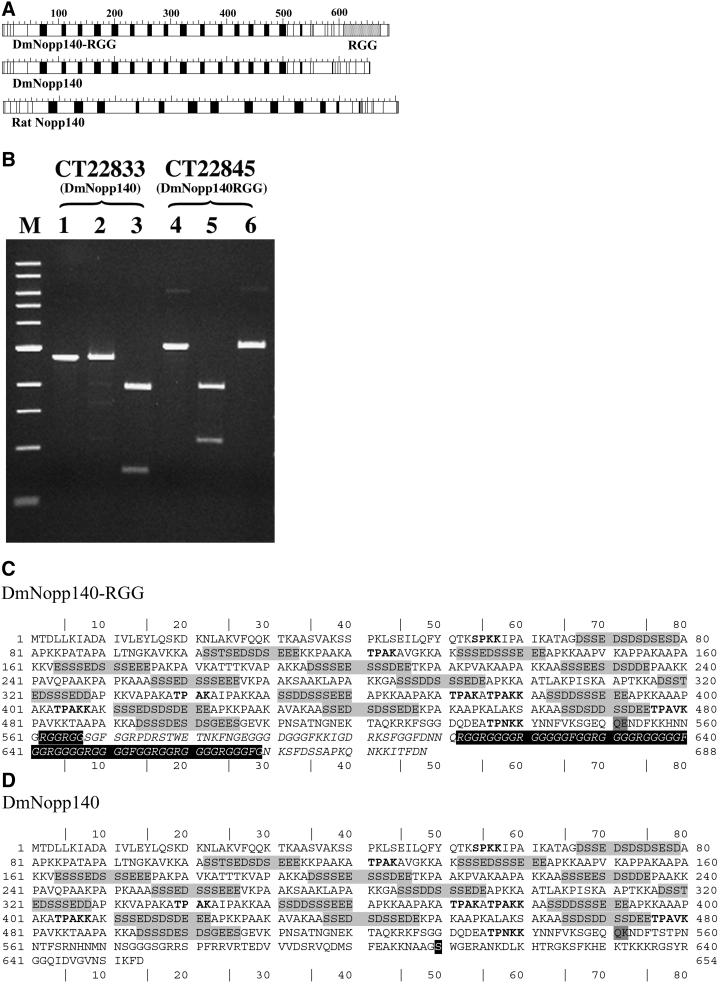
Sequence comparisons of DmNopp140-RGG and DmNopp140. (A) Acidic (black boxes) and basic (white boxes) regions alternate within the central domains of both Drosophila variants. This alternating pattern is similar to that within rat Nopp140. DmNopp140 is the Drosophila homolog of mammalian Nopp140, whereas DmNopp140-RGG is unique due to its carboxyl-terminal RGG domain. (B) Expressed sequence tags exist for both Drosophila variants. Restriction maps allowed us to predict digestion patterns and thus to verify the clones. The purified cDNA insert that encodes conceptual transcript 22833 (DmNopp140) was left undigested (lane 1), incubated with PvuI that failed to cut as predicted (lane 2), or digested with AvaI that generated two bands of predicted size (lane 3). The purified cDNA insert that encodes conceptual transcript 22845 (DmNopp140-RGG) was left undigested (lane 4), incubated with PvuI that generated two predicted fragments (lane 5), or incubated with AvaI that failed to cut as expected (lane 6). The digestion patterns confirmed the existence of two separate cDNA clones. (C) The deduced amino acid sequence of DmNopp140-RGG. CT22845 consists of three exons. The first encodes amino acids 1–34, the second encodes 35–551, and the third encodes 552–688. The serine-rich acidic regions are highlighted in light gray. MPF phosphorylation motifs are in bold. The RGG domain spans residues 612–669. Two additional upstream RGG motifs reside at 562–567. (D) The deduced amino acid sequence of DmNopp140. CT22833 consists of four exons. The first two exons are identical to those in CT22845. Thus, the two proteins are identical up to residue 551 (dark gray box), after which their sequences diverge. The third exon in CT22833 encodes residues 552–604 and the fourth exon encodes residues 605–654. The carboxy terminus of DmNopp140 is 64% identical to the carboxy terminus of rat Nopp140. A highly conserved serine residue within this terminus (residue 610 in the black box) is a putative substrate site for cAMP-dependent protein kinase.