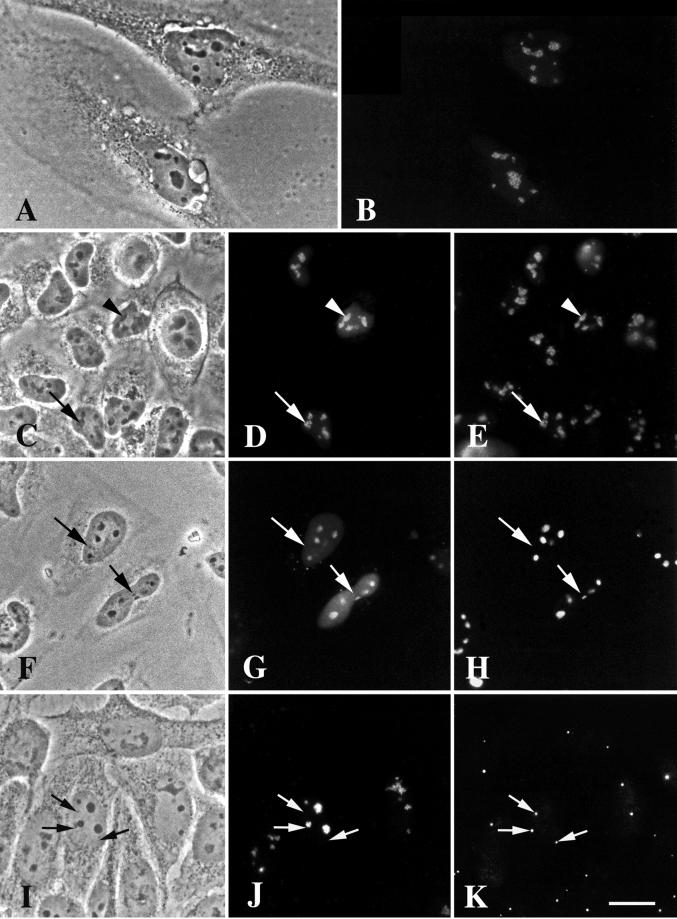
Figure 5.
DmNopp140-RGG localizes to intact, phase-dark nucleoli but fails to localize to endogenous Cajal bodies in transfected HeLa cells. (A and B) GFP-DmNopp140-RGG (B) localized to nucleoli in a punctate staining pattern. (C–E) Exogenous GFP-DmNopp140-RGG (D) colocalized with endogenous fibrillarin (E) that was detected with the S4 anti-human fibrillarin antibody and a rhodamine-conjugated secondary antibody. Arrowheads in C–E point to nucleoli that contain relatively large amounts of DmNopp140-RGG, whereas arrows in C–E point to nucleoli that maintain a punctate staining pattern with moderate amounts of DmNopp140-RGG. (F–H) Exogenous GFP-DmNopp140-RGG (G) colocalized with endogenous nucleolin (H) that was detected with an anti-nucleolin antibody and a rhodamine-conjugated secondary antibody. Arrows in F–H point to nuclear bodies that fail to stain with DmNopp140-RGG or anti-nucleolin. Conversely, all labeled structures evident in B, D, and G corresponded well to phase-dark nucleoli in A, C, and F, respectively. (I–K) Exogenous GFP-DmNopp140-RGG (J) again localized to intact phase-dark nucleoli, but it failed to colocalize with coilin in endogenous CBs as detected by the anti-human coilin antibody R288 (K). Precisely aligned arrows point to endogenous CBs. Bar (A–K), 20 μm.