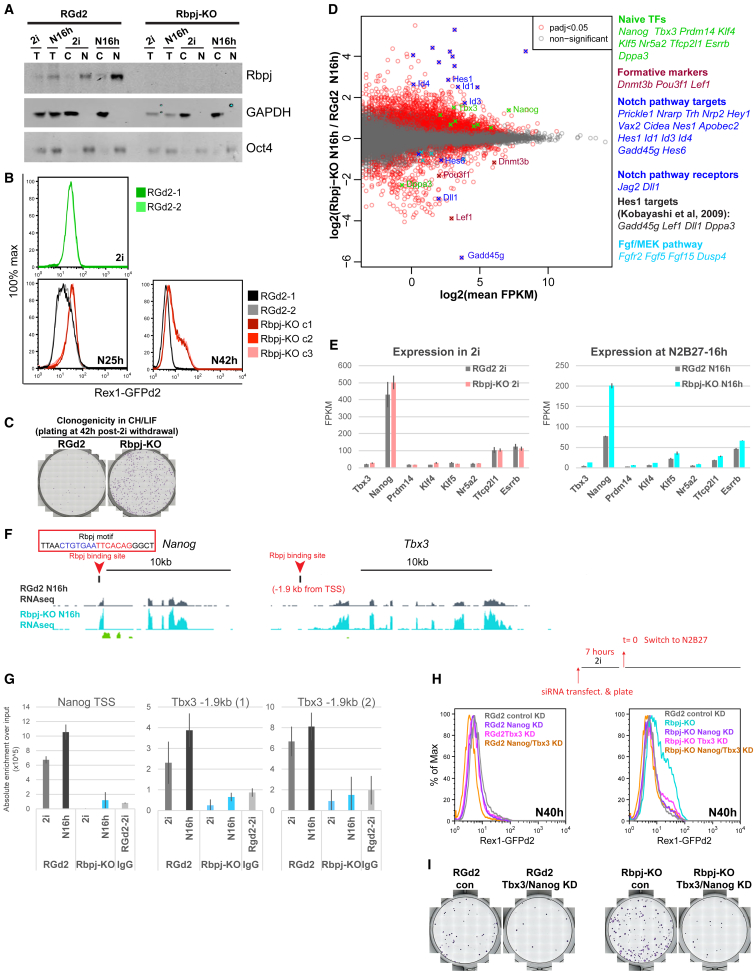
Figure 2.
RBPJ Expression and Function
(A) RBPJ western blot: C, cytoplasmic fraction; N, nuclear fraction; T, total cell lysate. Oct4 and GAPDH were used as loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively.
(B) GFP profiles of RGd2 and three clonal Rbpj mutant lines in N2B27 at 25 h (N25h) and 42 h (N42h) post-2i withdrawal.
(C) Colony assay.
(D) MA plot showing mean expression against fold change per gene in Rbpj-KO ESCs at 16 h post-2i withdrawal (N16h). Gene symbols and colored tags are shown for selected genes listed.
(E) RNA-seq expression values for naive pluripotency factors in RGd2 and Rbpj-KO ESC in 2i and at N16h. Error bars show SD from biological replicates plated in parallel; 3 independent clonal lines for Rbpj-KO and 2 different lines for RGd2 (one parental and one clonal).
(F) The University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) genome browser tracks for Nanog and Tbx3 loci showing normalized RNA-seq read coverage for parental and Rbpj-KO ESCs at N16h. RBPJ binding sites are indicated with red arrowheads. The RBPJ-binding motif within the Nanog locus is highlighted.
(G) ChIP-qPCR for binding sites shown in Figures 2F and S4E. Two primer sets were used for the Tbx3 locus. y axis shows absolute enrichment normalized to input DNA for each sample. Error bars indicate SD from two ChIP replicates.
(H) GFP profiles at 40 h after 2i withdrawal following a 7-h period of siRNA transfection.
(I) Colony assay at 40 h after 2i withdrawal.
See also Figures S2, S3, and S4 and Tables S1 and S2.