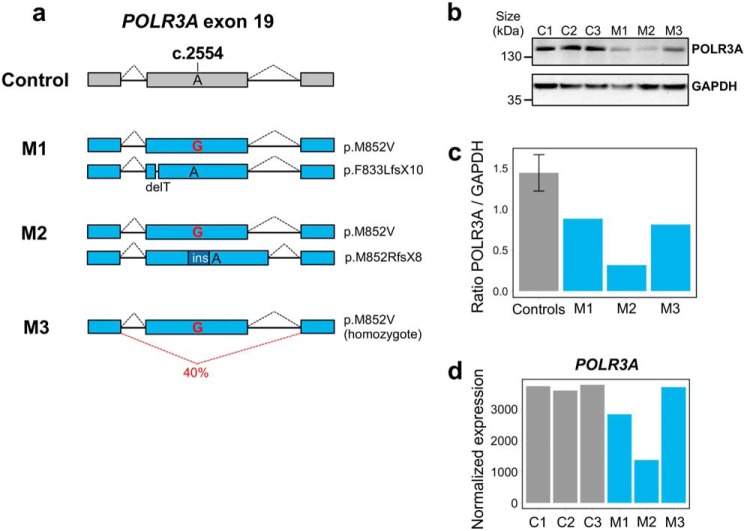
Figure 1.
Characterization of POLR3A mutant clones obtained by CRISPR-Cas9. a, schematic of the genotypes in POLR3A mutant clones. Mutants M1 and M2 are compound-heterozygous for the M852V mutation and a deletion/insertion leading to a premature stop codon. The predicted protein change is indicated on the right. Mutant M3 is homozygous for the M852V mutation, but this results in partial exon 19 skipping at the mRNA level (see Fig. S2 for details). Exon and intron sizes are not at scale. b, POLR3A protein levels in control and mutant clones. GAPDH was used as a loading control. c, quantification of POLR3A protein levels normalized to GAPDH levels. The three controls were grouped together. d, POLR3A mRNA levels in control and mutant clones, quantified by RNA-seq. Mutant M3 has normal levels of POLR3A mRNA, suggesting exon 19 skipping does not affect mRNA stability. ins indicates insertion.