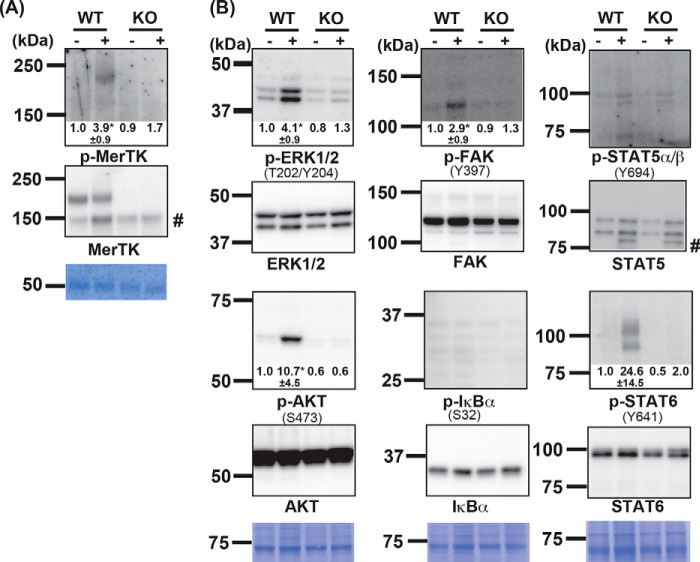
Figure 3.
Activation of signaling molecules induced by apoptotic cells. Adherent resident peritoneal cells (2.0 × 106 cells) from WT or MerTK−/− (KO) mice were incubated at 37 °C for 10 min with (+) or without (−) 1.0 × 107 apoptotic thymocytes, washed with PBS, and lysed in lysis buffer. A, MERTK was immunoprecipitated with anti-MERTK, dissolved in SDS sample buffer, and one-quarter of the aliquots were analyzed by Western blotting with an HRP anti-phosphotyrosine mAb (top panel) or a biotinylated anti-MERTK Ab followed by incubation with HRP–streptavidin (center panel). The membrane was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB, bottom panel). B, cell lysates from 1.5 × 106 cells were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against the indicated phosphorylated (top panel) or nonphosphorylated molecules (bottom panel), followed by HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG. The phosphorylated amino acid residues recognized by the antibody are indicated in parentheses. Membranes were stained with CBB (bottom panel). #, nonspecific band. The western blots were performed several times, and the band intensity of the phosphorylated kinase was quantitated by densitometry. When addition of apoptotic thymocytes in WT macrophages caused an apparent change in band intensity, the -fold change is shown with S.D. *, p < 0.03; Student's t test.