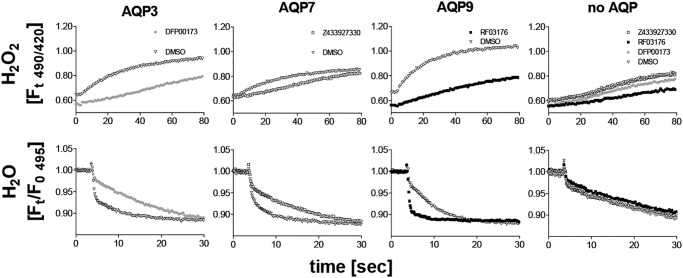
Figure 4.
Shown are H2O2 permeability (top row) and water permeability (bottom row) in H2O2 sensor (HyPer-3)–expressing CHO cell lines. Expression of mAQP3, mAPQ7, and mAPQ9 conferred a faster fluorescence increase in response to H2O2 addition (150 μm), compared with control cells (no AQP). Addition of cognate inhibitors resulted in a slower fluorescence increase in AQP-expressing cell lines after H2O2 addition, whereas no clear effects on control cells (no AQP) were observed. Similarly, AQP inhibitors reduced water permeability in AQP-expressing cell lines only (cell shrinking in response to sucrose addition 3.6 s into each read). The same HyPer-3–expressing cell lines were loaded with calcein before water permeability measurements. We note that the calcein fluorescence intensity is about 10-fold higher than HyPer-3 fluorescence under the conditions used. HyPer-3 did not seem to interfere with water permeability measurements. Furthermore, we noted a small baseline fluorescence decrease induced by DFP00173 and RF03176 treatment that was present before H2O2 addition. The reason for this effect is unknown. Means of four recordings are shown.