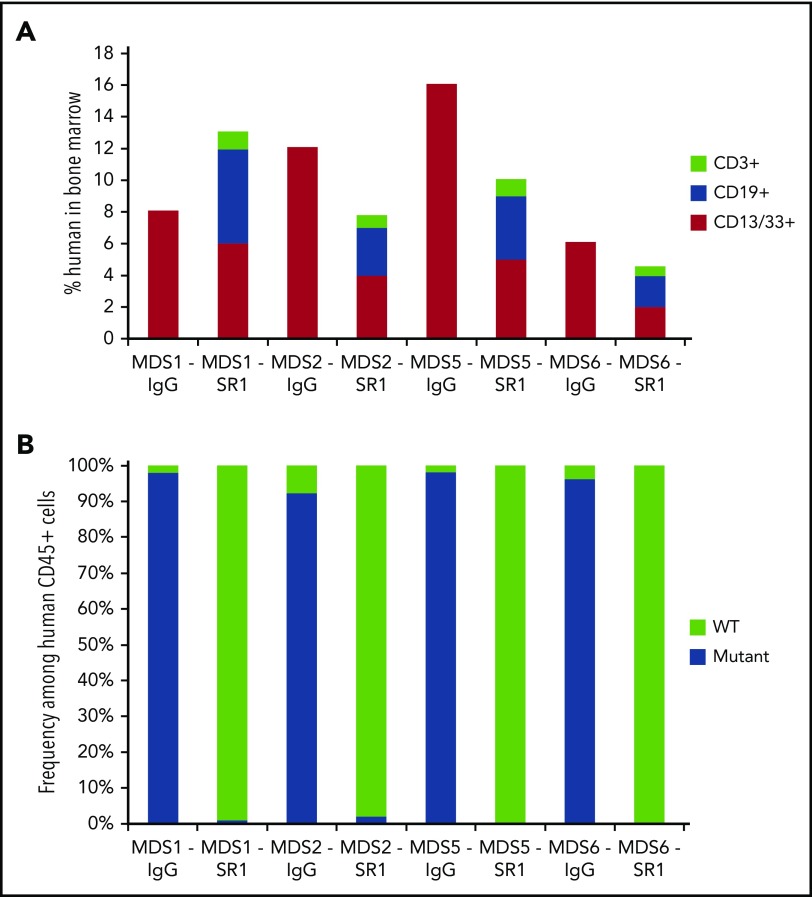
Figure 3.
SR-1 permits engraftment of second human UCB HSC graft in low-risk MDS-xenografted mice. (A) Total human chimerism (human CD45+) as well as distribution of myeloid (human CD45+CD13/33+), B-cell (human CD45+CD19+), and T-cell (human CD45+CD3+) chimerism in BM of low-risk MDS-xenografted mice treated with control isotype IgG antibody or SR-1 mAb on day 1, 3, 5, and 7, and then transplanted on day 15 with a second normal human UCB HSC graft. Chimerism was measured 12 weeks after second normal human UCB HSC transplant (n = 4, IgG treated; n = 4, SR-1 treated). (B) Frequency of cytogenetically abnormal clones (−Y, del(20q), or +8), as detected by FISH within human cells FACS-isolated from BM of low-risk MDS-xenografted mice treated with IgG control antibody or SR-1 mAb on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 and then transplanted on day 15 with a second normal human UCB HSC graft. Cells were analyzed 12 weeks after second normal human UCB HSC transplant (n = 4, IgG treated; n = 4, SR-1 treated).