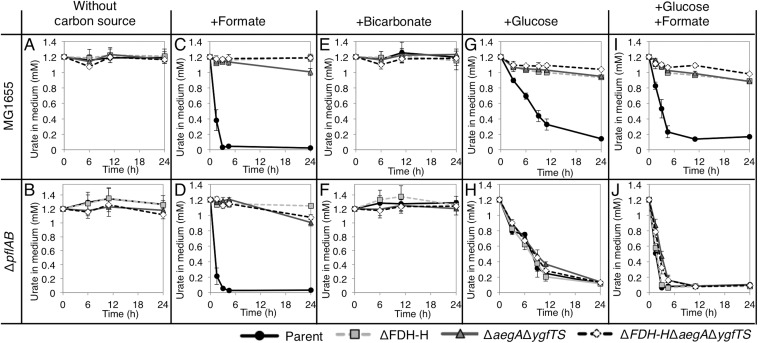
FIG 6.
The effect of various carbon sources on uric acid degradation. (A and B) The amount of uric acid in an unsupplemented minimal medium (without any carbon source) during a 24-h incubation of wild-type derivatives (A) and ΔpflAB derivatives (B). (C and D) The effect of the supplementation of a minimal medium with formate on the amount of uric acid in the medium during a 24-h incubation of wild-type derivatives (C) and ΔpflAB derivatives (D). (E and F) The effect of the supplementation of a minimal medium with bicarbonate on the amount of uric acid in the medium during a 24-h incubation of wild-type derivatives (E) and ΔpflAB derivatives (F). (G and H) The effect of the supplementation of a minimal medium with glucose on the amount of uric acid in the medium during a 24-h incubation of wild-type derivatives (G) and ΔpflAB derivatives (H). (I and J) The effect of the supplementation of a minimal medium with glucose and formate on the amount of uric acid in the medium during a 24-h incubation of wild-type derivatives (I) and ΔpflAB derivatives (J).