FIG 8.
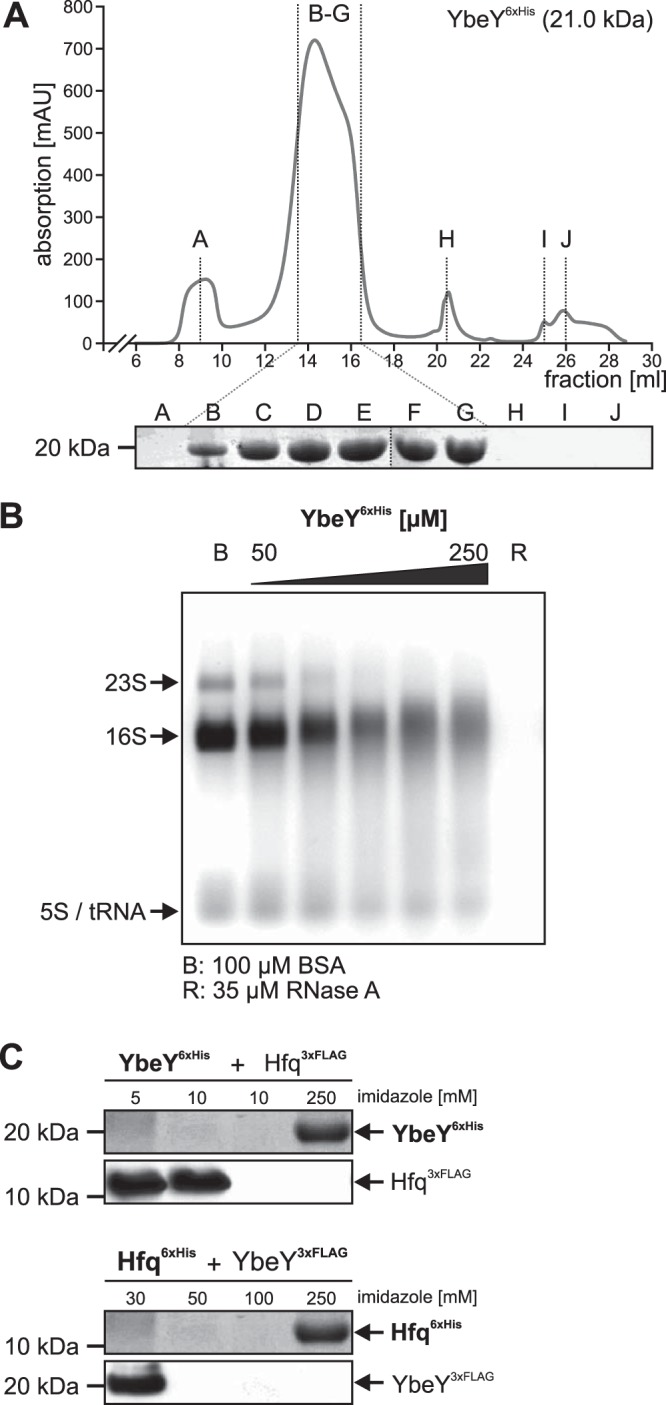
Purification and biochemical analyses of A. tumefaciens. (A) GPC with YbeY6×His (20.6 kDa, C-terminally tagged) resulted in a distinct protein peak with a maximum absorption of 719.5 mAU at 14.3 ml, indicating elution of 34- to 86-kDa large protein complexes, which corresponded to homo-oligomers of two to four YbeY6×His monomers. Protein abundance in fractions B to G was verified by SDS-PAGE. (B) RNase activity of purified YbeY. Various amounts of N-terminally tagged YbeY6×His protein (50 to 250 μM) were incubated with 5 μg total RNA from A. tumefaciens WT. Lane B, 100 μM BSA; lane R, 35 μM RNase A. (C) Pulldown experiments of YbeY6×His and Hfq3×Flag protein variants from cell extracts after incubation for 30 min on ice. YbeY6×His was bound by the Ni-NTA column, whereas Hfq3×Flag was washed off the column by low imidazole concentrations (5 to 10 mM). YbeY6×His was eluted with 250 mM imidazole. Western blot analysis with specific His- or Flag-tagged antibodies did not show coelution of Hfq3×Flag protein with YbeY6×His. Similar results were obtained when protein tags were switched between both proteins (YbeY3×Flag and Hfq6×His).
