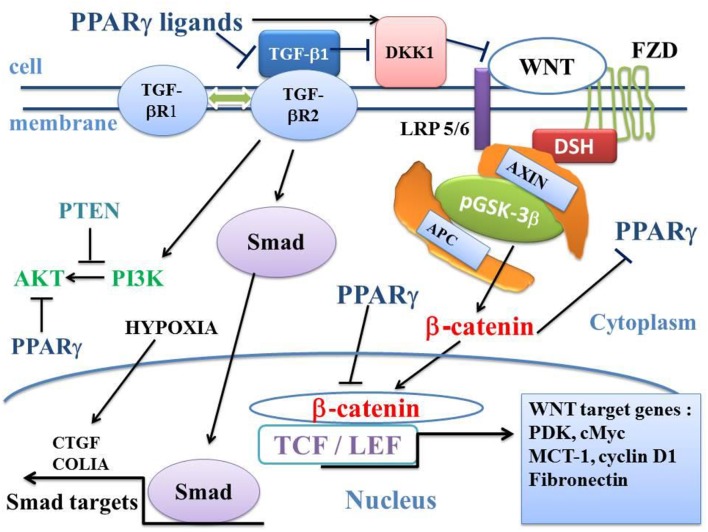
Figure 3.
Influence of TGF-β1 on the balance between the canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling and PPARγ. In the presence of the WNT ligands, the WNT receptor binds both LRP5/6 and FZD receptors to initiate LRP phosphorylation and DSH-mediated Frizzled internalization. This leads to the dissociation of the GSK-3 β/AXIN/APC destruction complex. Phosphorylation of β-catenin is inhibited and β-catenin accumulates in the cytosol and then translocates to the nucleus to bind TCF-LEF transcription factors. This leads to the WNT-response gene transcription (PDK, MCT-1, cMyc, and Cyclin D1). PPARγ inhibits the β-catenin/TCF-LEF-induced activation of WNT target genes. TGF-β also enhances WNT signaling through the inhibition of DKK1. DKK1 is activated by PPARγ. TGF-β1 binds type 2 TGF-βR2 receptor (TGF-βR2), which recruits type 1 TGF-βR1 receptor (TGF-βR1). This results in the formation of a heterotetramer that phosphorylates Smad. The Smad complex then translocates to the nucleus and regulates the transcription of target genes (CTGF, COL1A). A non-Smad pathway also occurs through PI3K-AKT. PTEN inhibits PI3K-AKT and PPARγ inhibits AKT. APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CTGF, Connective tissue growth factor; DKK1, Dickkopf-1; DSH, Disheveled; FZD, Frizzled; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; LRP5/6, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; MCT-1, monocarboxylate lactate transporter-1; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and AKT, AKT/Protein Kinase B; PTEN, Phosphatase and tensin homolog; PDK, pyruvate; dehydrogenase kinase; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor; TGF, Transforming Growth Factor.