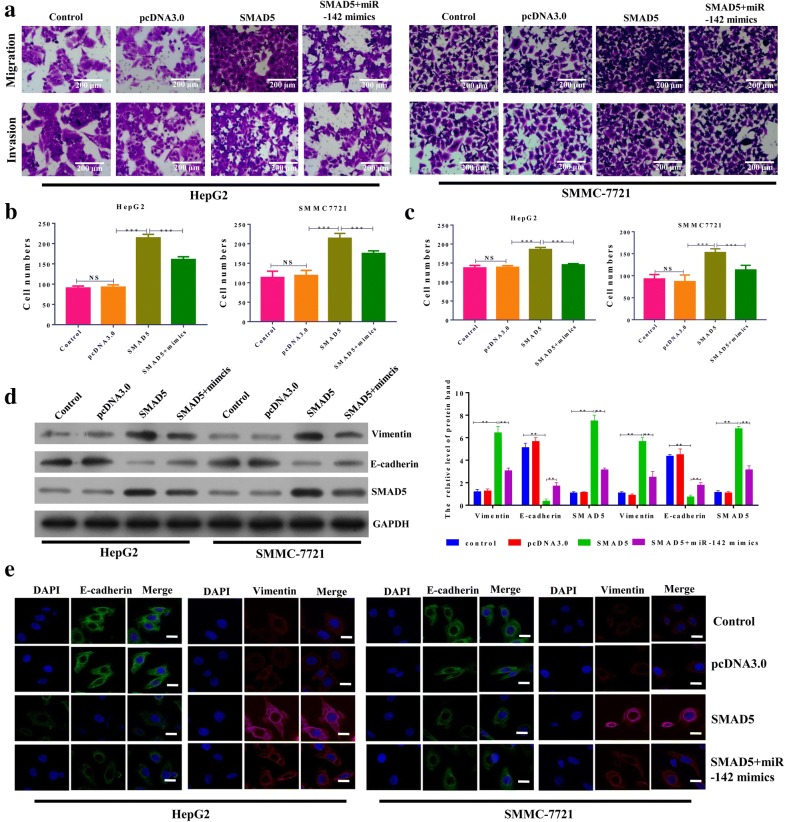
Fig. 5.
MiR-142-3p suppressed the migration, invasion and EMT by targeting SMAD5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. SMAD5 was ectopically expressed in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells by a plasmid containing SMAD5. The plasmid vector pcDNA3.0 was used as control. The miR-142-3p mimic control mimic (NC) was also used as indicated in the figure. a The cell migration assay and matrigel invasion assay were performed to assess the migration potency of HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells after the transfection indicated in the figure. Representative images of the invaded cells are shown. Magnification, ×200. b After the cell migration assay, six fields within each chamber were photographed using an inverted microscope and camera, and migrating cells were counted in each field. The average number is shown. c After the matrigel invasion assay, six fields within each chamber were photographed using an inverted microscope and camera, and invading cells were counted in each field. The average number is shown. d The protein expression of vimentin, SMAD5 and E-cadherin in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells after the indicated transfection for 48 h was performed by Western blot. The densitometry plot of results from the blots is shown. The relative expression levels were normalized to GAPDH. e Immunofluorescence assay was used to assess the protein levels of vimentin and E-cadherin in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells after the indicated transfection. Scale bar, 10 μm. Data represent three independent experiments (mean and SEM of triplicate samples). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GAPDH; EMT, epithelial cell-to-mesenchymal transition; SEM, standard error of the mean