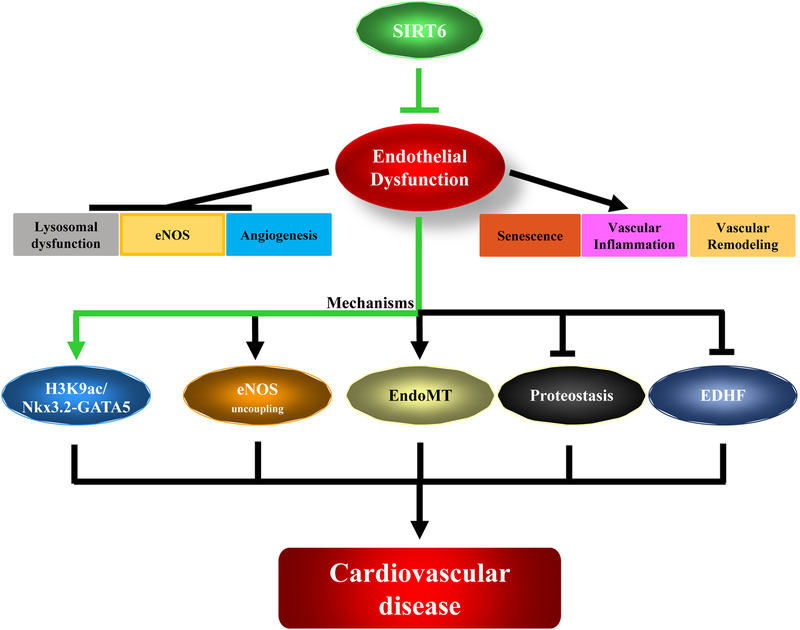
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of endothelial dysfunction and its influence on function and mechanisms of ECs. Highlighted in green is the conclusion according to Jian Guo and colleagues. Endothelial dysfunction impairs proteostasis, eNOS functions, and angiogenesis and promotes senescence, vascular inflammation and remodeling of ECs. Several Mechanisms including regulation of Nkx3.2-GATA5 signaling, eNOS uncoupling, endothelium to mesenchymal transition (EndoMT), impaired proteostasis and EDHF have been uncovered to emphasize the importance of endothelial dysfunction and its causative role in cardiovascular diseases.