FIGURE 1.
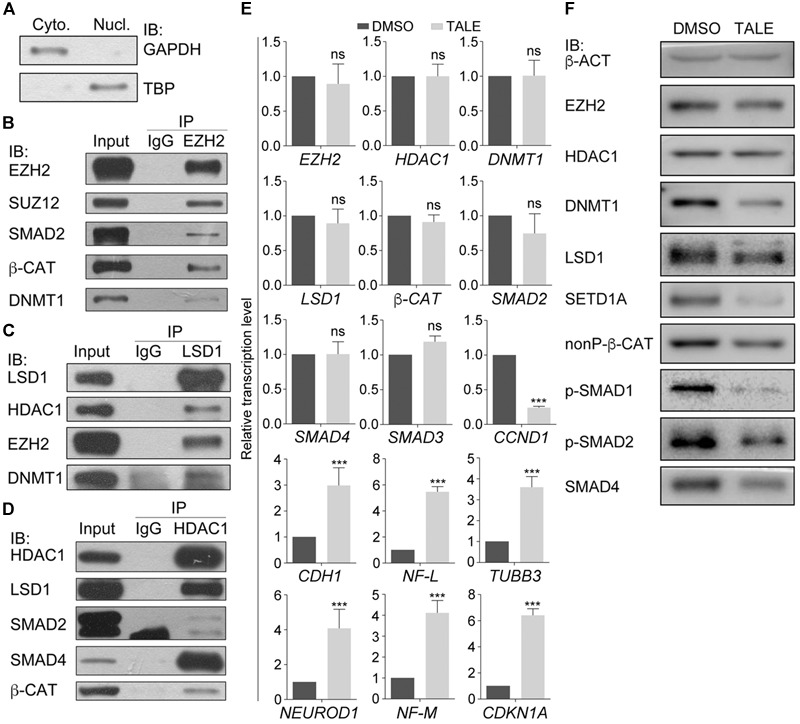
Protein interactions in cancer cell lines and differential effect of combined chemical inhibition on gene expression and protein. (A–D) Chromatin modification enzymes and signal transducers forms interactions in HepG2 cell nuclei. (A) Immunoblotting (IB) detection of the effect of nuclear protein extraction. GAPDH was used as a marker for cytosolic fraction (Cyto.) and TBP was used as a marker for nuclear fraction (Nucl.). (B–D) Different proteins were detected from the immunoprecipitates that were precipitated from the nuclear lysates with the antibody against EZH2 (B), LSD1 (C), and HDAC1 (D). In each experiment in (B–D), co-IP with an IgG antibody was performed in parallel as a negative control, and the protein level in the nuclear lysates was used as positive control (Input). (E) TALE treatment caused different regulatory effect on transcription of genes, as examined with qRT-PCR. Significance in gene expression change was calculated for experiments in triplicate using Student’s t-test. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ns, not significant. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (F) Immunoblotting detection of protein level in cell without (DMSO) and with TALE treatment. β-ACT was used as a loading control.
