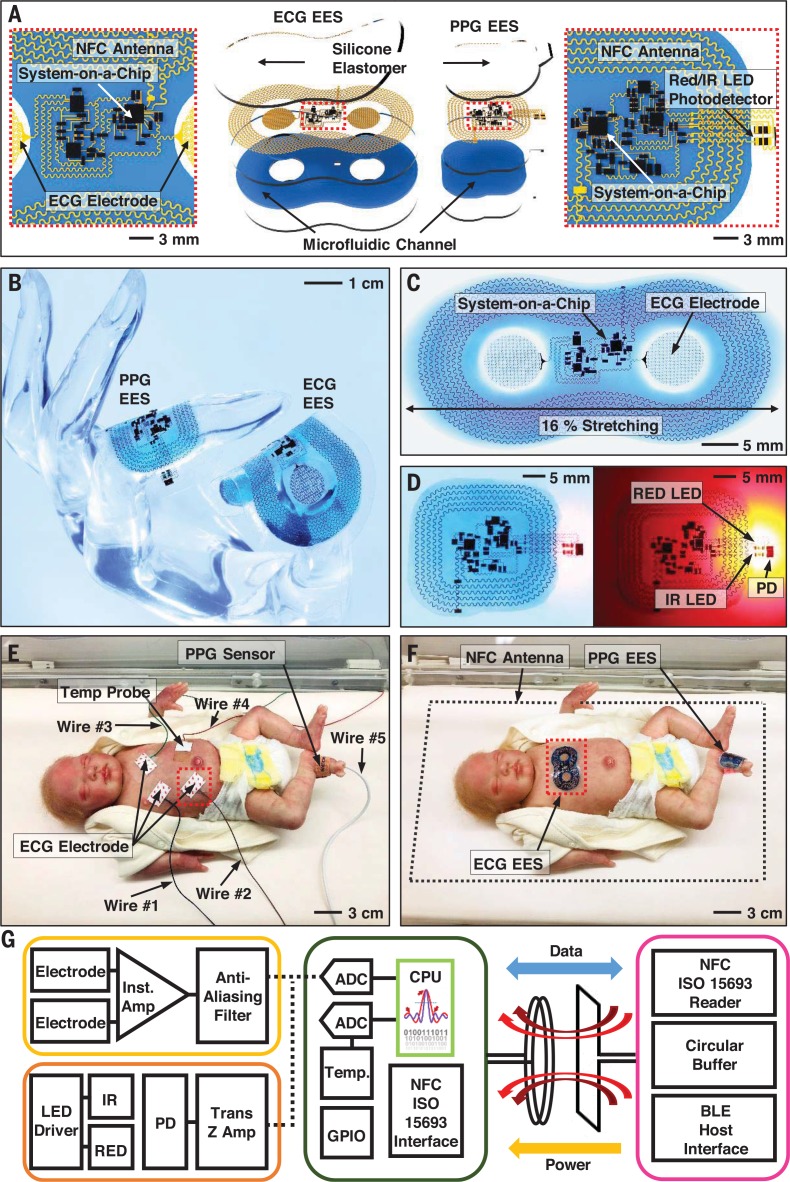
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustrations and photographic images of ultrathin, skin-like wireless modules for full vital signs monitoring in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) with comparisons to clinical-standard instrumentation. (A) Schematic illustration of wireless, battery-free modules for recording electrocardiogram (ECG) and photoplethysmogram (PPG) data and skin temperature. The ionic liquid in the microfluidic channel contains blue dye for visualization purposes. (B) Images of devices draped over the fingers of a life-sized, transparent mannequin hand to illustrate the sizes and physical form factors of these devices. (C) Image of an ECG EES stretched uniaxially in the horizontal direction by ~16%. (D) Device for capturing PPG data during operation in a lighted and a dark room. PD, photodiode. (E and F) NICU setting with a life-sized neonate doll configured with conventional measurement hardware (E) and with a binodal (chest and foot) deployment of skin-like wireless devices designed to provide the same functionality and measurement fidelity (F). (G) Functional block diagram showing analog front end of each EES, components of the NFC SoC including microcontroller, GPIO, and radio interface, with a host reader platform that includes an NFC reader module and a BLE interface with circular buffer.