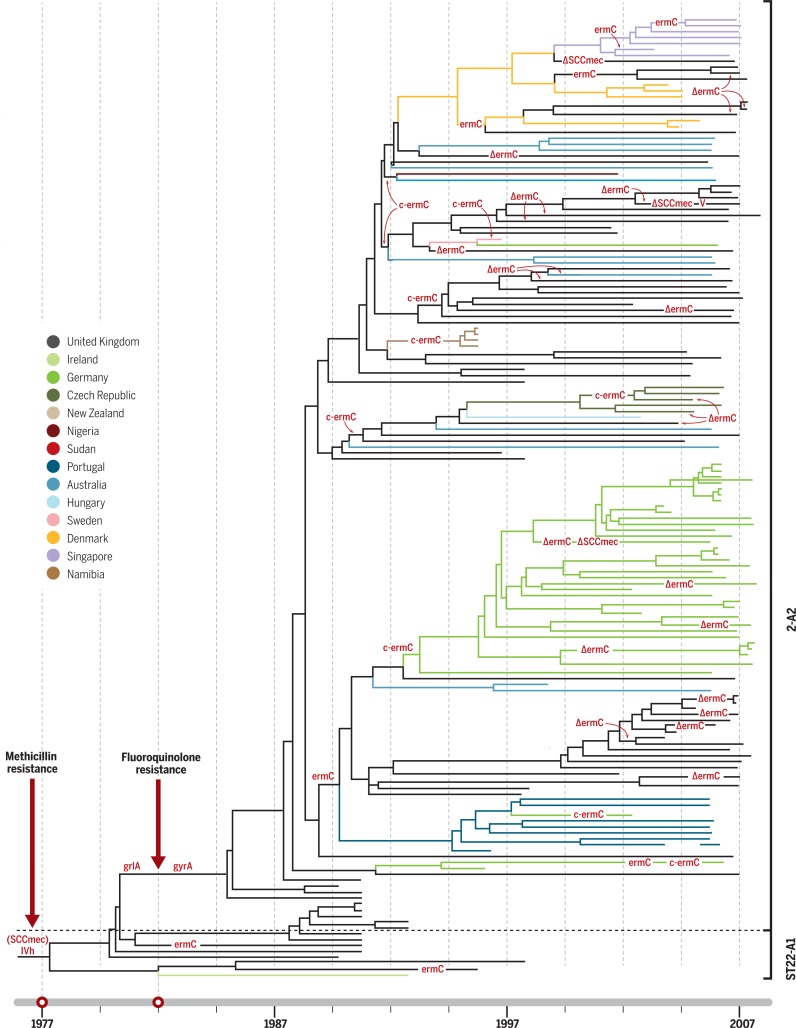
Fig. 1.
The time line of the ST22 MRSA pandemic. Bayesian phylogenetic tree reconstructing the ST22 MRSA pandemic over a 30-year period (8). Maximum clade credibility tree of ST22 MRSA based on BEAST analysis using a variable clock rate (uncorrelated lognormal) model. Tips of the tree are constrained by isolation dates; the time scale is shown at the base of the tree. Gains and losses (D) of genetic determinants for resistance to methicillin (SCCmec), fluoroquinolones (point mutations in grlA and gyrA), erythromycin (plasmid-encoded ermC), and clindamycin (mutations in ermC leader peptide region, c-ermC) have been mapped on the tree by applying the parsimony criterion. The figure depicts two pivotal events: the acquisition of methicillin resistance around 1977 and fluoroquinolone resistance in 1982 (red arrows). This clone then underwent rapid international spread, including countryspecific clonal expansions; countries highlighted in color.