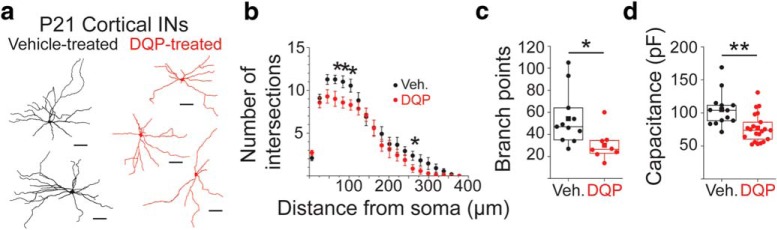
Figure 7.
In vivo blockade of GluN2C/D-containing NMDARs from P7–P9 leads to long-term reductions in IN dendritic arbor complexity. a, Representative projections of reconstructed INs in the cortex at P21 after treatment from P7–P9 with DQP (red, n = 8 cells/4 animals) or vehicle (black, n = 11 cells/3 animals). b, Sholl analysis using 2 d projections of reconstructed INs to quantify the number of intersections at increasing distances from the soma from 10 to 580 μm in 30 μm intervals. *p < 0.05 (two-sample t test). Data are mean ± SEM. c, Box-and-whisker plot showing quantification of total branch point number made on 3 d reconstructed neurons. Box boundaries indicate quartiles. Scatterplot of solid circles represents individual data points. Solid squares represent group means. **p = 0.015 (two-sample t test). d, Box-and-whisker plot showing quantification of capacitance from INs at P21 that were treated with DQP-1105 (n = 21 cells/7 animals) or vehicle (n = 13 cells/4 animals) from P7–P9. Box boundaries indicate quartiles. Scatter plot of solid circles represents individual data points. Solid squares represent group means. **p = 0.0019 (two-sample t test).