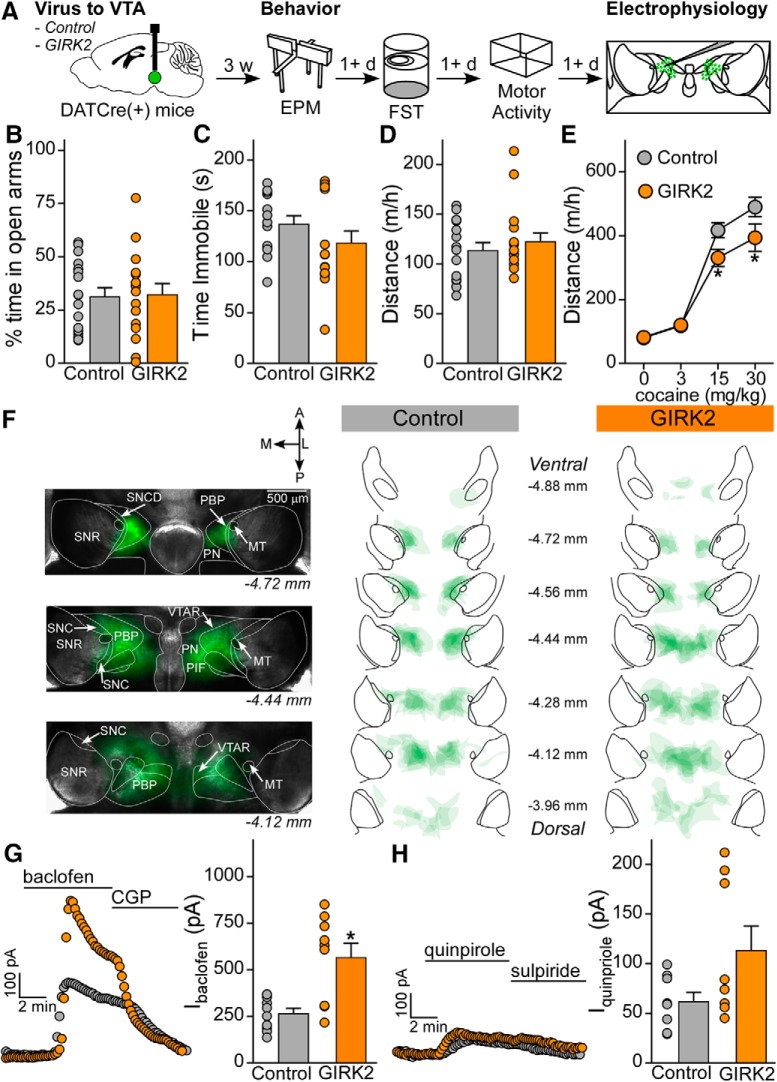
Figure 4.
Viral enhancement of GIRK channel activity in VTA DA neurons decreases behavioral sensitivity to cocaine. A, Schematic of experiment, in which DATCre(+) mice were injected with control of GIRK2 virus. Three weeks following surgery, mice were tested for EPM, FST, and cocaine locomotor activity, with each task separated by at least 1 d. Following behavior, mice were processed for placement and electrophysiology validation. B, EPM percent time in open arms is not different in control mice (n = 17, 31 ± 4%) and GIRK2 mice (n = 16, 32 ± 5%; t test, t(31) = 0.1446, p = 0.8860). C, FST time immobile during the final 4 min of the task does not differ between control mice (n = 13, 137 ± 8 s) and GIRK2 mice (n = 15, 119 ± 12 s; Mann–Whitney U test, U = 76, p = 0.3334). D, Distance moved on the handling habituation day was not different between control mice (n = 16, 114 ± 8 m/h) and GIRK2 mice (n = 16, 123 ± 9 m/h; Mann–Whitney U test, U = 119, p = 0.7487). E, Distanced traveled following injection of 0, 3, 15, and 30 mg/kg cocaine resulted in interaction between cocaine dose and virus (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, F(3,90) = 3.054, p = 0.032; Bonferroni post hoc test for 15 mg/kg, t = 2.548, p = 0.012, for 30 mg/kg, t = 2.824, p = 0.006). F, Representative images of viral spread in horizontal slices from a mouse in the control condition, imaged at 2× just before electrophysiology, and summary of viral spread for all mice in control and GIRK2 conditions. MT, Medial terminal nucleus of the accessory optic tract; SNC, substantia nigra, compact part; SNCD, substantia nigra, compact part, dorsal tier; SNR, substantia nigra, reticular part; PBP, parabrachial pigmented nucleus of the VTA; PIF, parainterfascicular nucleus of the VTA; PN, paranigral nucleus of the VTA; VTAR, ventral tegmental area, rostral part. G, GABABR-GIRK currents in the GIRK2 condition (n = 9 cells from 7 mice, 566 ± 77 pA) are significantly higher than those in the control condition (n = 10 cells from 7 mice, 265 ± 28 pA; Mann–Whitney U test, U = 14, p = 0.010). H, D2R-GIRK currents are not significantly different in control (n = 8 cells from 5 mice, 62 ± 9 pA) and GIRK2 conditions (n = 8 cells from 7 mice, 113 ± 25 pA; Mann–Whitney U test, U = 19.50, p = 0.207). *p < 0.05.