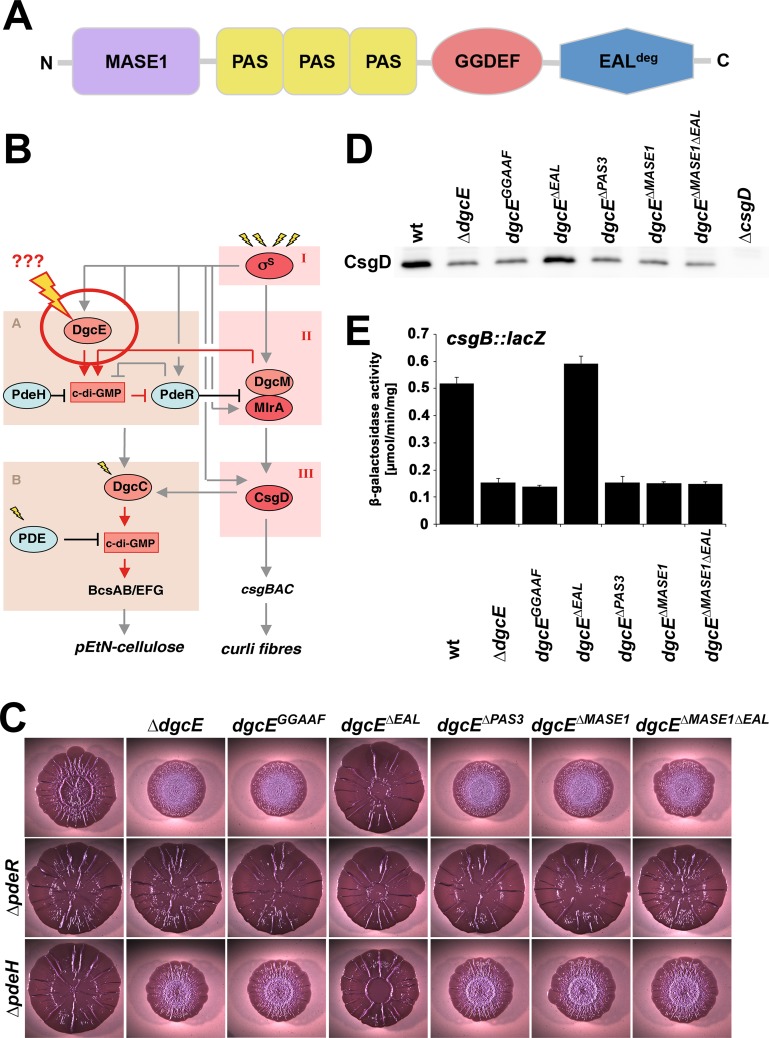
Fig 1. Role of domains in DgcE function.
A: Domain structure of DgcE. B: Regulatory network controlling the production of curli fibres and pEtN-cellulose. The vertical 'backbone' of the network is the transcription factor cascade σS/MlrA/CsgD (in red), with c-di-GMP input occurring via modules A and B, which include the integrated action of different DGCs and PDEs (in light red and light blue, respectively). DgcE is the master DGC at the top level of this hierarchy, with its signal input and processing (indicated by the bolt) being the central topic of this study. C: Macrocolonies of AR3110 derivatives with the indicated chromosomal dgcE alleles in otherwise wt, ΔpdeH and ΔpdeR backgrounds were grown on Congo red plates for 5 days at 28°C. D: CsgD levels determined by immunoblot analysis in strain AR3110 carrying the indicated chromosomal dgcE alleles. Samples were obtained at an OD578 of 3.6–3.8, with 6 μg total protein loaded per lane. E: csgB::lacZ expression measured after growth of strain W3110 Δlac(I-A) carrying the indicated chromosomal dgcE alleles in LB at 28°C for 24 h.