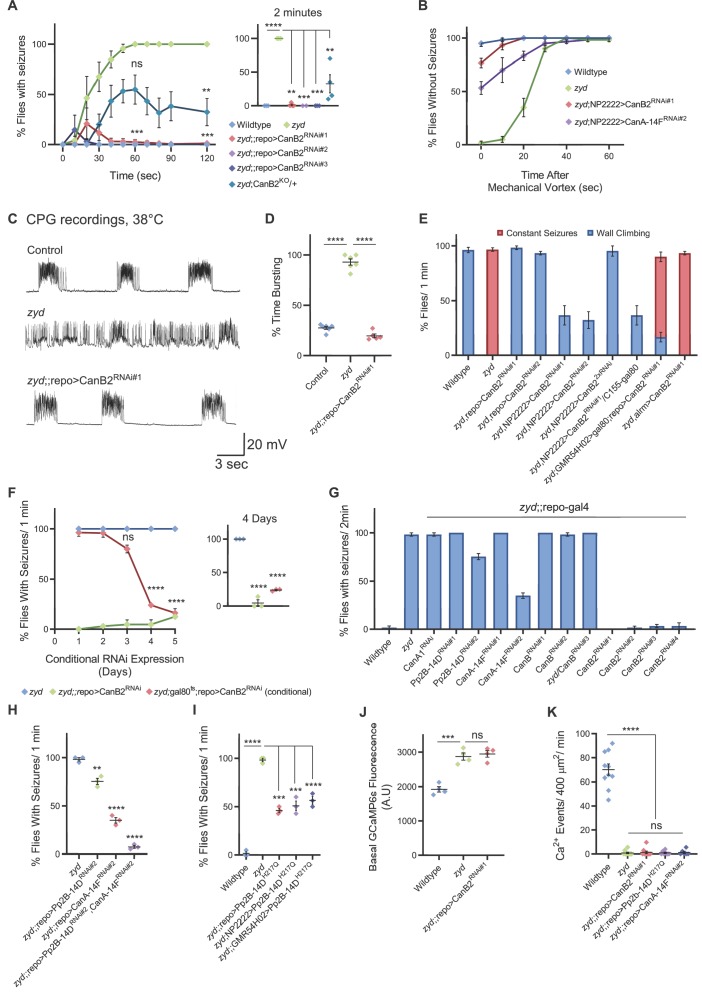
Figure 2. Cortex glial knockdown of calcineurin rescues zyd seizures without affecting intracellular Ca2+.
(A) Behavioral analysis of HS-induced seizures. Pan-glial knockdown of the CN regulatory subunit, CanB2, with three partially overlapping hairpins (#1, #2 and #3, see Materials and methods) completely rescues the zyd seizure phenotype, while a single copy of CanB2 knockout allele (CanB2KO/+) rescues ~60% of seizures (N = 4 groups of ≥15 flies/genotype). Inset shows analysis after 2 minutes of HS (p=0.0001). (B) Behavioral analysis of the recovery from vortex-induced seizures. Pan-glial knockdown of CanB2 and CanA-14F rescues zyd vortex-induced seizures (N = 3 groups of 20 flies/genotype). (C) Representative voltage traces of spontaneous CPG activity at larval 3rd instar muscle 6 at 38°C in wildtype, zyd and zyd;;repo >CanB2RNAi#1 animals (n ≥ 5 preparations/genotype). (D) Quantification of average bursting duration for CPG recordings of the indicated genotypes at 38°C (n ≥ 5 preparations/genotype). (E) Detailed analysis (see Materials and methods) of HS induced behaviors of zyd/CanB2RNAi flies. Cortex glial knockdown of CanB2 leads to seizure rescue in ~30% of zyd;NP2222>CanB2RNAi flies, with the remaining ~70% displaying partial rescue. Cortex glial CanB2 knockdown with two copies of the RNAi (zyd;NP2222>CanB22xRNAi) recapitulates the full rescue seen with pan-glial knockdown. Inhibiting gal4 expression of the RNAi in neurons with gal80 (C155-gal80) does not alter the rescue observed with cortex glial knockdown, and astrocyte specific (alrm-gal4) CanB2 knockdown does not rescue zyd seizures (N = 3 groups of >15 flies/genotype, see Figure 2—figure supplement 1D for complete dataset). (F) Cortex glial conditional knockdown of CanB2 using gal4/gal80ts. Rearing adult flies at the restrictive temperature (>30°C) for gal80ts allows expression of CanB2RNAi only at the adult stage. A significant reduction in seizures (p<0.0001) was seen after four days of rearing flies at the restrictive temperature for gal80ts (31°C), with only ~25% of adults showing seizures. The reduction in seizures was enhanced when adults were incubated at 31°C for longer periods (N = 3 groups of >10 flies/genotype). Inset shows analysis after 4 days of incubation at 31°C (p=0.0001). (G) Pan-glial knockdown of the Drosophila calcineurin (CN) family (CanA1, CanA-14D/Pp2B-14D, CanA-14F, CanB and CanB2) indicate CanB2 knockdown completely rescues zyd seizures, CanA-14D and CanA-14F knockdowns partially reduce seizures (N = 4 groups of >10 flies/genotype). (H) Pan-glial knockdown of Pp2B-14D and CanA-14F partially rescues the zyd HS seizures phenotype (~25% rescue for Pp2B-14D, p=0.0032; and ~60% rescue for CanA14F, p<0.0001). Knocking down the two genes simultaneously rescues zyd seizures, with only ~10% of flies showing seizures (~90% rescue, p<0.0001, N = 3 groups of >10 flies/genotype). (I) Overexpressing a dominant-negative form on Pp2B-14D (CanAH217Q) rescues ~50% of zyd seizures regardless of the driver used (repo: p<0.0001; NP2222: p=0.0006; GMR54H02- p=0.0004. N = 3 groups of >10 flies/genotype). (J) Larval Ca2+ imaging in cortex glia expressing myrGCaMP6s indicates the elevated basal Ca2+ fluorescence at 25°C observed in zyd mutants relative to wildtype cortex glia (p=0.0003) is not altered following CanB2 knockdown (zyd;;repo>CanB2RNAi, p=0.6096. n ≥ 5 animals/genotype). (K) Microdomain Ca2+ oscillations observed in wildtype cortex glia expressing myrGCaMP6s are abolished in zyd cortex glia and are not restored following either CanB2 or CanA14F knockdown (n ≥ 5 animals/genotype). Error bars are SEM, **=P < 0.01, ***=P < 0.001, ****=P < 0.0001, Student’s t-test.