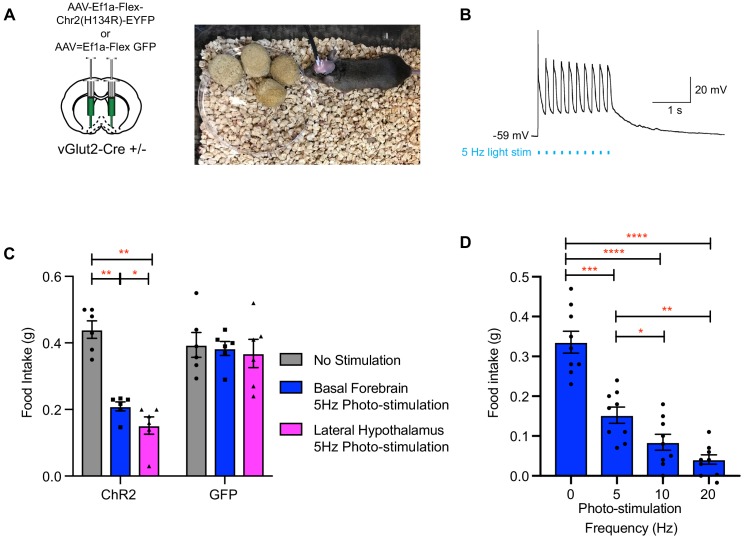
Figure 8. Photo-stimulation of vGlut2BF neuron cell bodies and vGlut2BF lateral hypothalamic projections decreases food-intake.
(A) Schematic showing viral injection into the basal forebrain (left), and a picture of a mouse with bilateral fiberoptic implants over both the basal forebrain and lateral hypothalamus (right). (B) Whole cell recordings from a channelrhodopsin expressing vGlut2BF neuron showing high fidelity activation with 5 Hz photo-stimulation. (C) Food intake of vGlut2BF channelrhodopsin or GFP expressing mice during 30 min of photo-stimulation. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Two-way RM ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison. N = 6 animals, three males/3 females. (D) Food intake of fasted vGlut2BF channelrhodopsin expressing animals implanted only over the basal forebrain and subsequently photo-stimulated only over the basal forebrain at various photo-stimulation frequencies. *p<0.05, **p,0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p,0.0001. RM One-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison, N = 9 animals, five males/4 females.