Figure 1.
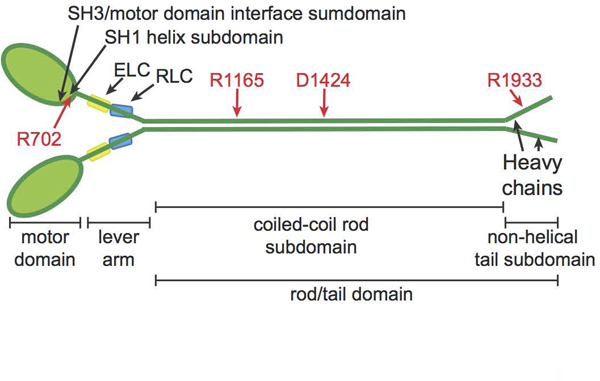
NMIIA molecule structure with domains and residues used in MYH9-RD genotype-phenotype comparisons. NMIIA heterohexameric molecules contain two heavy chains (green). Each heavy chain consists of an N-terminal motor domain with F-actin-activated ATPase activity, a flexible lever arm, a rod domain that mediates coiled-coil formation of the two heavy chains, and a non-helical tail with regulatory functions. MYH9-RD mutations occur in all domains, with motor domain mutations commonly in two subdomains: the SH3/motor domain interface and the SH1 helix. Each lever arm binds an essential light chain (ELC, yellow) and a regulatory light chain (RLC, blue). Four residues commonly affected by MYH9-RD mutations are denoted in red.
