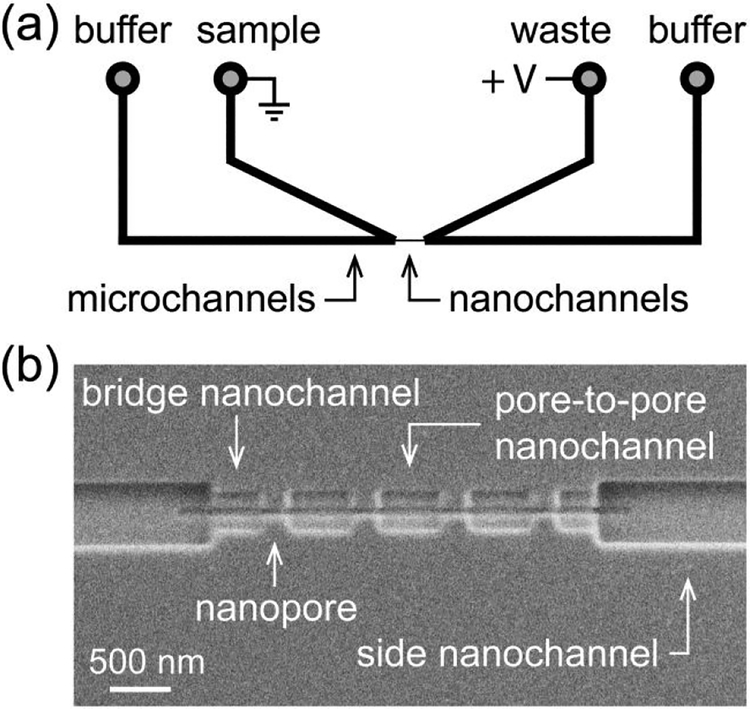
Figure 2. Schematic of nanofluidic device and scanning electron microscope (SEM) image.
(a) Two V-shaped microchannels are connected through a series of nanopores and nanochannels. (b) SEM image of the nanochannels and nanopores milled into the glass surface. The nanopores were 60 ± 5 nm deep, 60 ± 5 nm wide, and 290 ± 6 nm long for resistive-pulse measurements of the T = 3 capsids (31.3 nm in diameter), T = 4 capsids (35.7 nm in diameter), and their intermediates.