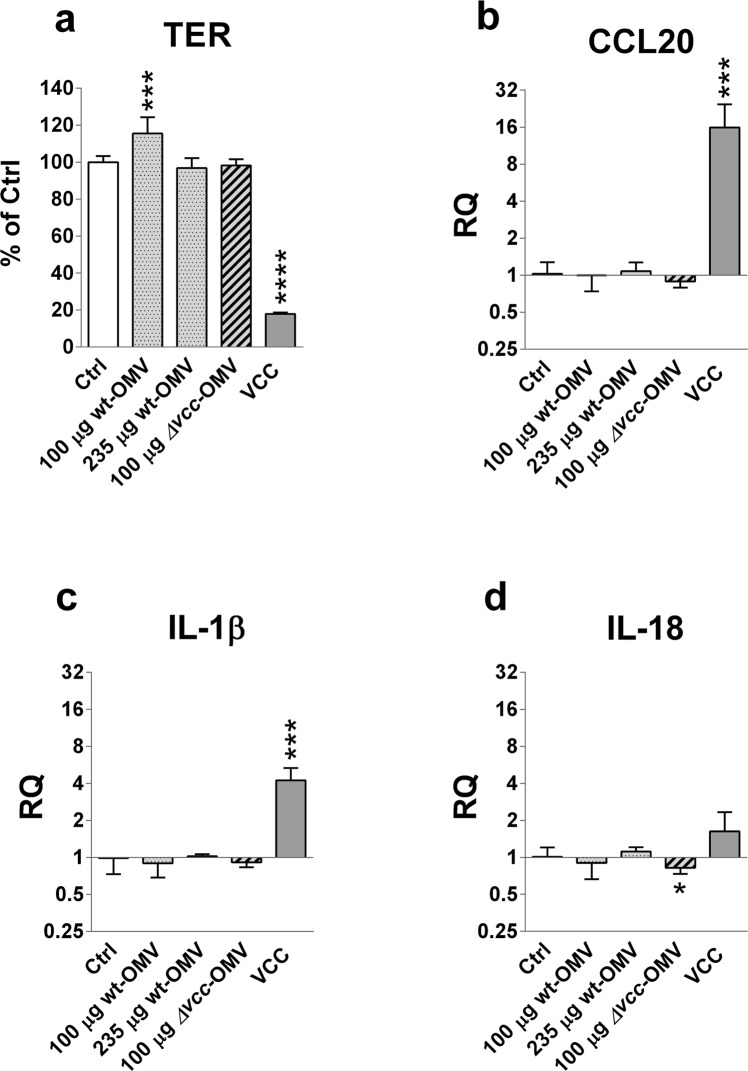
Figure 2.
Soluble VCC causes decreased TER and increased expression levels of CCL20 and IL-1β mRNA in T84 polarized tight monolayer cells, while OMV-bound VCC causes increased TER and no change in cytokine mRNA levels. Polarized tight monolayers of T84 cells were challenged at the apical side with density gradient centrifugation purified OMVs from the V. cholerae strain V:5/04 (wt-OMV-p) and its VCC deletion mutant (Δvcc-OMV-p). Monolayers were challenged with 100 µg wt-OMV-p/monolayer (100 µg wt-OMV, dotted bar; n = 12), 235 µg wt-OMV-p/monolayer (235 µg wt-OMV, dotted bar; n = 4), 100 µg Δvcc-OMV-p/monolayer (100 µg Δvcc-OMV, striped bar; n = 12) and 80 ng soluble VCC (VCC, grey bar; n = 4) or sham-treated monolayers (Ctrl, open bar; n = 16). (a) Changes in TER. (b–d) Changes in levels of mRNA for CCL20 (b), IL-1β (c) and IL-18 (d). Results in (a) are given as % of controls (% of Ctrl) for individual monolayers relative to the mean %TER of sham-treated control monolayers in the respective experiment. Results in (b–d) are given as relative quantity (RQ) compared to the median level of sham-treated control monolayers in the respective experiment. Challenges were done with the indicated amount of OMV protein/monolayer for 5 hours. Three batches of wt-OMV-p and Δvcc-OMV-p, respectively, were tested in 3 independent experiments. n = number of monolayers. Bars indicate mean + 1 SD. Statistically significant differences are shown; ****P-value < 0.0001, ***P-value < 0.001, *P-value < 0.05.