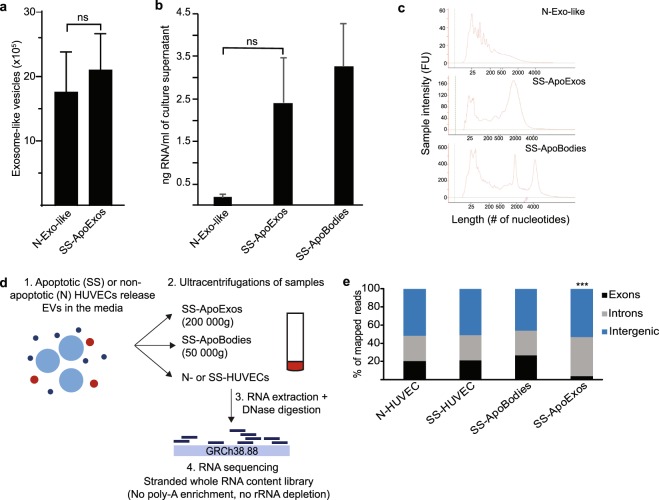
Figure 1.
Features of EVs produced by normal and apoptotic HUVECs. (a) Normal and apoptotic HUVECs generate similar amounts of exosome-like vesicles. Small particle flow cytometry analysis of CMFDA stained exosome-like vesicles released by HUVECs cultured in standard (N) or serum-starved (SS) condition and isolated from the same volume of culture media (two-tailed unpaired T test, p = 0.7, n = 4). (b) Vesicles released by apoptotic HUVECs contain more RNA. Bioanalyzer quantification of RNA extracted from EVs released by SS-HUVECs (SS-ApoExos and SS-ApoBodies) vs. N-HUVECs (N-exo-like vesicles); two-tailed unpaired T test, p = 0.098, n = 2. (c) Vesicles released by N-HUVECs contain small or fragmented RNAs. Bioanalyzer profiles of RNA extracted from EVs released by SS-HUVECs (ApoExos and ApoBodies) vs. N-HUVECs (N-exo-like vesicles). (d) Workflow for generation and isolation of EVs and for RNA extraction and sequencing. See Methods for details. (e) Distribution of RNA-Seq reads in ApoExos. STAR mapped RNA-Seq reads were categorized as exonic, intronic or intergenic using RSeQC 2.6.3. ApoExos contain significantly more intronic sequences and less exonic sequences than apoptotic bodies (***Two-tailed Fisher exact test, p = 1.1 × 10−5) and HUVECs (**Two-tailed Fisher exact test, p = 3 × 10−3).